Ballasted roofs: why gravel, and how to protect their waterproofing
Something of an innovation in the Italian building scene, while also being a useful device for protecting the roof, the ballasted flat roof is a solution that can become a distinctive feature of either a residential or commercial building.
Unlike the traditional system involving the use of concrete, using gravel is an option that brings a number of attractive advantages:
- it protects the roof against wind and UV rays
- it protects the roof against mechanical damage
- it is low maintenance
- it provides thermal comfort in summer as it shades the roof
- it makes the whole roof system practically fireproof
- it is long lasting.
In building, the choice of a ballasted roof is often prompted by aesthetic reasons for a holiday home or a hotel by the sea, or in an area with high sunshine hours… while it also caters to the need for optimal insulation and low maintenance.
The TeMa Building Solutions answer for protecting ballasted roofs
When gravel is laid, the load can tear the waterproofing layer on the roof underneath, and this comes with the risk of leaks, with all the ensuing stain, mould and structural damage issues.
So it is important to address the need for rainwater drainage and mechanical protection of the waterproofing.
TeMa Building Solutions has come up with a product that serves multiple functions: the product in question is T-Kone G Drain, the studded membrane (which serves to protect the waterproofing) featuring a geotextile (addressing the need for filtration and separation).
Placed between the gravel layer and waterproofing, T-Kone G-Drain is thin, strong and ideal for an effective build-up without the bulk.
- Published in Ballasted roofs, BUILDING, Studded membranes and accessories
Green surfaces and green roofs: benefits and technical ins and outs
In recent years, “green” has become more and more of a buzzword, encompassing simple and cost-effective solutions that can be adopted by anyone with a roof. We’re talking green roofs, which, in addition to bringing undeniable environmental benefits, are the perfect place for relaxing with the family or enjoying summer drinks with friends. The origins of roof gardens date back to ancient times — think Hanging Gardens of Babylon — and, today, are built for extreme reliability, including long service life, with excellent products producing even more advantages.
Let’s take a look at the full picture in detail.
The advantages of green areas
For the environment
Plants and grass are natural carbon sinks, absorbing CO2 and releasing oxygen, in addition to filtering particulate matter. In addition, they lessen the urban microclimate effect by lowering temperatures by several degrees centigrade, and reduce electrosmog caused by any electronic device.
They muffle noise and, if designed well, absorb and retain the early sudden downpours associated with significant rain events.
A series of sustainable improvements for urban wellbeing, improving air quality with less smog and particulate matter.
For occupant comfort
Vegetation also acts as natural thermal insulation — which is no small advantage given the energy crises of recent months — and soundproofing in loft bedrooms. Furthermore, it provides the roof with effective protection against UV rays, mechanical stress and daily variations in temperature, thus increasing the average service life of waterproofing.
Lastly, creating a garden on a roof increases the value of the property.
From a technical point of view
A green roof build-up comprises a number of layers, including geosynthetics offering better performance than traditional systems in terms of drainage, mechanical protection of waterproofing, and filtration. The products used are lighter and non-bulky, easy to transport and quick to install.
Functions required of the roof
There are 4 main functions involved:
- Reservoir (to hold rainwater for irrigation purposes until it is needed) and drainage (to remove excess water). This combined function is addressed with 20mm HDPE studded membranes T-Kone H XL and T-Kone H XL S.
- Control of surface erosion caused by atmospheric agents. This function is addressed with natural fibre matting T-Juta 500 and the synthetic geomat T-Mat.
- Drainage. This is where T-Mix Drain 20 SS comes in, the cuspated-fibre geomat sandwiched between 2 geotextiles.
- Mechanical protection of waterproofing. The geotextiles from the Tematex NW PET range, in white and black, fit the bill.
- Published in BUILDING, Flat green roofs
Rooftop car park: next-level solution for making the most of underused space.
City centres are overcrowded with vehicles and restricted areas, car parks are “stressed” and there are never enough spaces to go round. Alongside the more “standard” trafficable ceiling slab solutions — such as in the case of underground garages — it’s not too much of a stretch, where structurally feasible, to think about designing or making better use of spaces on elevated levels.
Over the holidays, car parks on the roofs of public buildings or buildings for use by the public could also provide refuge for the cars of passers-through. During the offices’ closing time, for example, these parking spaces can become a real asset, an ideal solution for making use of otherwise unused space and increasing the number of car parks for people travelling to tourist hot spots
Continual vehicular traffic and exposure to the elements — from freezing temperatures to sweltering heat — mean the construction materials used must be fit for purpose. Intensive use means it’s imperative all the proper layers are in place (build-up design) to serve the different specific functions. Let’s see what these layers are.
What do we need to be careful about when designing a rooftop car park?
This kind of roof is subjected to high loads, both static and dynamic, from vehicles of all kinds. This makes the mechanical protection of the waterproofing layer and the need for high compressive strength two key focus areas.
Drainage is another aspect to be factored into the design. Rainwater can seep into the underlying layers and damage them, so we need to ensure that water is drained off the roof properly.
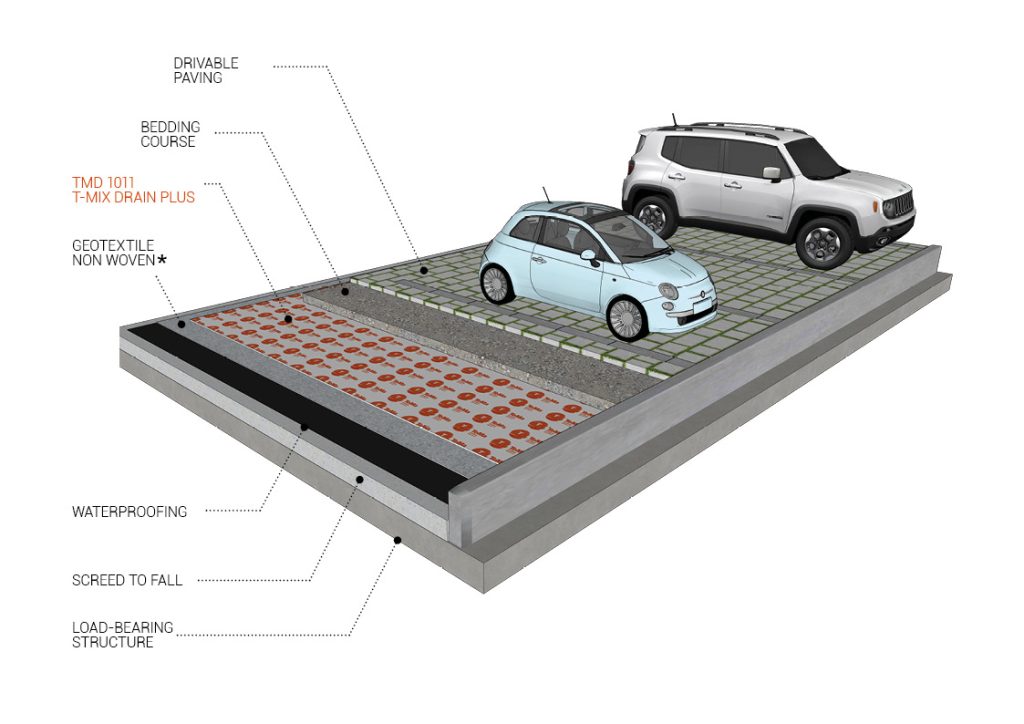
We recommend applying studded membranes laminated with nonwovens or drainage geocomposites made from monofilaments or geonets.
Our drainage geocomposite T-Mix Drain Plus is a good candidate for the drainage layer. Alternatively, you can opt for the T-Net Drain 5 and T-Net Drain 7 geonets, which are sandwiched between nonwovens.
The job of mechanical protection, together with drainage, can instead be handled by the drainage geocomposite TMD 1011. The product consists of a filter geotextile laminated to a studded membrane, whose conformation delivers effective drainage even under the strain of high loads (up to 400 kPa).
- Published in BUILDING, Drainage geocomposites
The roof: problems to be tackled and solutions to be adopted
“A hole in the roof is enough to ruin a home.”
So the (Italian) saying goes. Of course, there may not be any holes in the roof in the strict sense of the word, but, unfortunately, in a broad sense there might be. Roofs are subject to problems such as water seepage, damp and, in the case of trafficable flat roofs or car park roofs, heavy loads.
The roof is the part of a building directly exposed to weather conditions, such as rain, snow and hail, but also to heavy loads. It’s the least visible part of the house and the most difficult to inspect. When building a roof, it’s therefore essential to consider factors that might affect its integrity and safety, as well as harm the health of occupants.
Water seepage leads to damp and peeling walls. Dampness means mould and unhealthy attic environments.
So, let’s take a look at the main problems and see what solutions can be found.
Water seepage
Ponding on a roof will wet and ruin the materials used. It’s therefore necessary to install a drainage system for rainwater or, in the case of trafficable flat roofs, for accidental leaks of oil or fuel from vehicles. This applies to green roofs, trafficable flat roofs and ballasted flat roofs.
Solutions need to be found that don’t increase the “load” on the roof.
Solutions
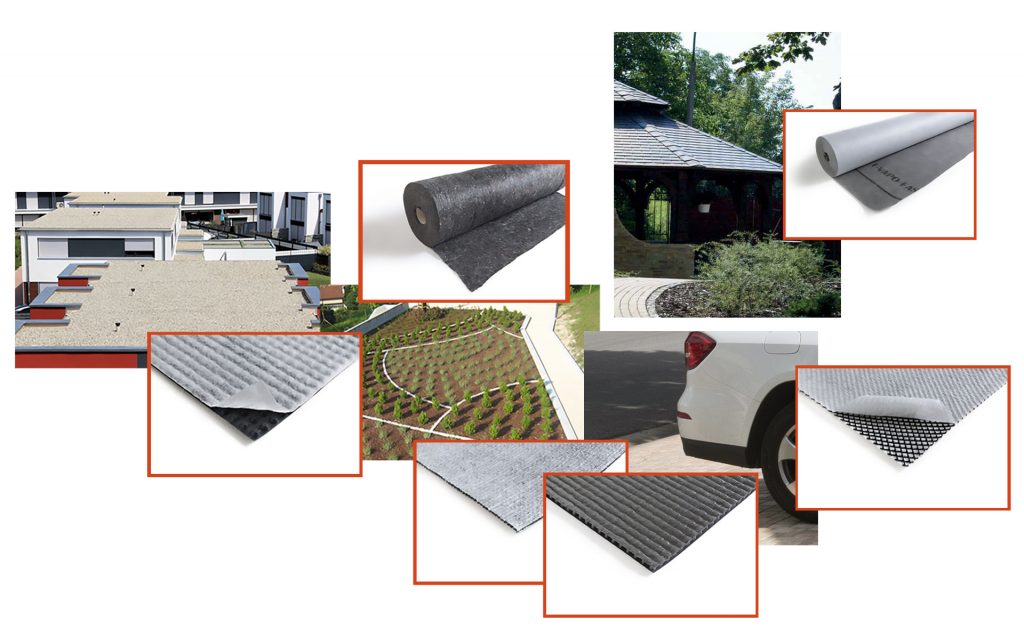
TeMa Building Solutions recommends installing its drainage geocomposite , T-Mix Drain Plus and TMD 1011, ideal for trafficable flat roofs and flat green roofs; its T-Kone G Drain studded membrane, suitable for ballasted flat roofs and flat green roofs; or T-Net Drain geonet for trafficable flat roofs.
Vapour control
It’s also necessary to focus on vapour control. Due to temperature differences between the air and the roof material, there’s a risk of condensation forming. To prevent this, highly waterproof vapour diffusion membranes need to be laid.
Solutions
The membranes in the T-Vapo range act as a barrier, retarder and vapour diffuser for pitched roofs.
Mechanical protection of waterproofing
The first step is to ensure that the waterproofing layer is intact and remains that way. Any cracks, cuts or inaccurate application in corners can cause irreparable damage to the underlying surface, requiring major intervention and considerable costs. By the time damp patches appear, the damage is often already severe.
Moreover, in the case of roofs used as parking areas or flat green roofs, the heavy weight that the materials need to withstand must be considered.
Solutions
TeMa Building Solutions proposes its T-Kone G Drain studded membrane and the Tematex range of geotextiles for flat green roofs.

- Published in BUILDING, Drainage geocomposites, Studded membranes and accessories