System for reinforced soil retaining structures
T-System is the system from TeMa Geo Solutions that includes various components for strengthening, surface erosion control, drainage and retaining used in the construction of reinforced soil retaining structures: innovation that we’ve been exploring here at TeMa since our inception 30 years ago, and that is now one of our hallmarks. Let’s take a more detailed look below.
Components for strengthening
Designed for strengthening, the knitted X-Grid PET C geogrids are made from high-strength polyester yarn, with a protective polymer coating. They deliver tensile strength in the 20 kN/m to 800 kN/m range.
Components for erosion control
They protect the face of the structure from erosive agents, like wind and driving rain, until the vegetation has had time to establish. TeMa Geo Solutions offers natural solutions made from cellulose fibres, like Ecovermat, or jute fibres, like Ecovernet, as well as synthetic solutions made from monofilaments (K-Mat F), polypropylene (K-Mat FA) or fibreglass (K-Mat FG Green).
Components for drainage
Drainage geocomposites like Q-Drain are used to address the problem of water seeping into the backfill.
Components for retaining
We have a line of facings made from electrically welded wire mesh — with inclinations ranging from 65° to 80° — to ensure the exposed face is straight.
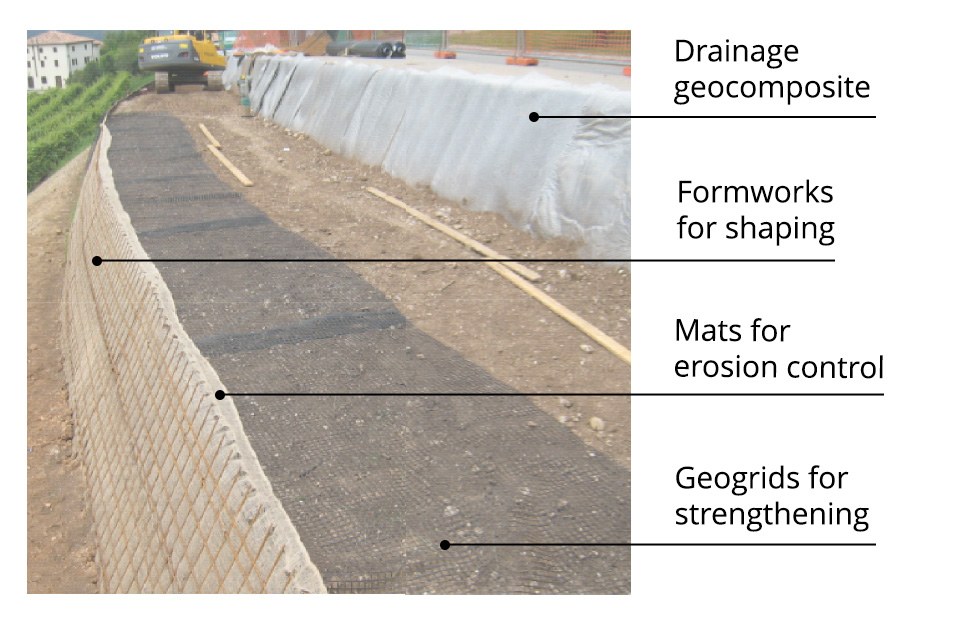
Practical tips
On site
System components must be stored well away from machinery, and suitably protected from dust or residues from work on site.
To avoid excessive overlaps and waste, the X-Grid geogrids must be cut to size using a suitable metal stand with metal trestles supporting a circular rod to be inserted inside the roll.
Erosion control components — whether biodegradable or synthetic — must be stored in a dry place and not in direct contact with the natural ground, so as to avoid laying problems later on.
Metal formwork must be stored well away from areas where machinery is operating, and carried in only when it is time to install.
During assembly, it is best to apply U-shaped strips of rubber or metal so that the geogrids can be wrapped correctly over the formwork without getting caught on the top of the bars. (see photo)
Special instructions
We advise against backfilling with silty and clayey material; at the very least, only use this kind of material after mixing it with aggregate.
The full range of system components comes with instructions on the relevant procedures to be followed. Contact us, we’ll be happy to provide case studies and full information.
- Published in Erosion mats, GEO, Geogrids, news, Reinforced earth structures, Reinforced earth structures - Drainage, Reinforced earth structures - Erosion control
Sustainable finance: sustainable development
It’s interesting to realize just how much the environmental culture of a business can be a way to accelerate its development, even by allowing it to access finance that’s vital for its growth and innovation: this is where the concept of sustainable finance comes in.
No self-respecting company report is complete without covering sustainability, the circular economy, wellbeing and the environment, which have different connotations for different businesses and are promoted to varying extents over the course of their lives.
The fact that this has become a “mature” issue can be seen in the need and, indeed, the will of companies to meet the requirements of ESG “certification” (Environmental, Social and Governance), since those companies who are attuned to these worlds are destined to have a more productive future and be more attractive to financial backers.
So, by sustainable finance we mean finance that supports the capital and investments of businesses with future-proof projects, especially from an environmental point of view. This is a practice aimed at investing to develop production processes, in addition to funding research into raw materials and end-of-life disposal of products, with the upstream decision process generally focusing on protecting the planet.
The cornerstones of sustainable finance
There are three factors taken into consideration, into which the tangible application of sustainable development can be narrowed down.
- Environmental factors: these include issues like the need to promote greener, more energy-efficient production processes. They very much hinge on the themes of circular economy and zero-emission activities, as well as on preventing pollution and protecting biodiversity.
- Social factors: these focus more on reducing inequality and on developing an inclusive system, one that is pro-human rights, in addition to investing in training and in the wellbeing of communities.
- Governance factors: these ensure that both environmental and social factors are included in the company‘s decision-making processes.
TeMa and sustainability
TeMa Technologies and Materials has long been a believer in using sustainable materials and creating sustainable solutions, even in the building and geotechnical fields.
Reinforced soil projects, on both a small and large scale, are a case in point: the technique of using soil as a retaining material, instead of concrete, certainly makes the structure more environmentally friendly, providing benefits in terms of both the landscape and liveability (they often double as noise barriers, click here for more information).
We provide 30-plus years of experience in the development of geogrids and geomembranes supplied in rolls, which are easy to carry to even the most inaccessible sites, and are ideally suited to the construction of landfills, tunnels, roads, reinforced soil projects and drainage ditches.
In addition to the many advantages in terms of construction, they come with the no small benefit of energy savings and the reduction in air pollution achieved when using geomembranes instead of traditional gravel: in terms of transport alone, the number of trips (trucks) drops from 100 to 1.
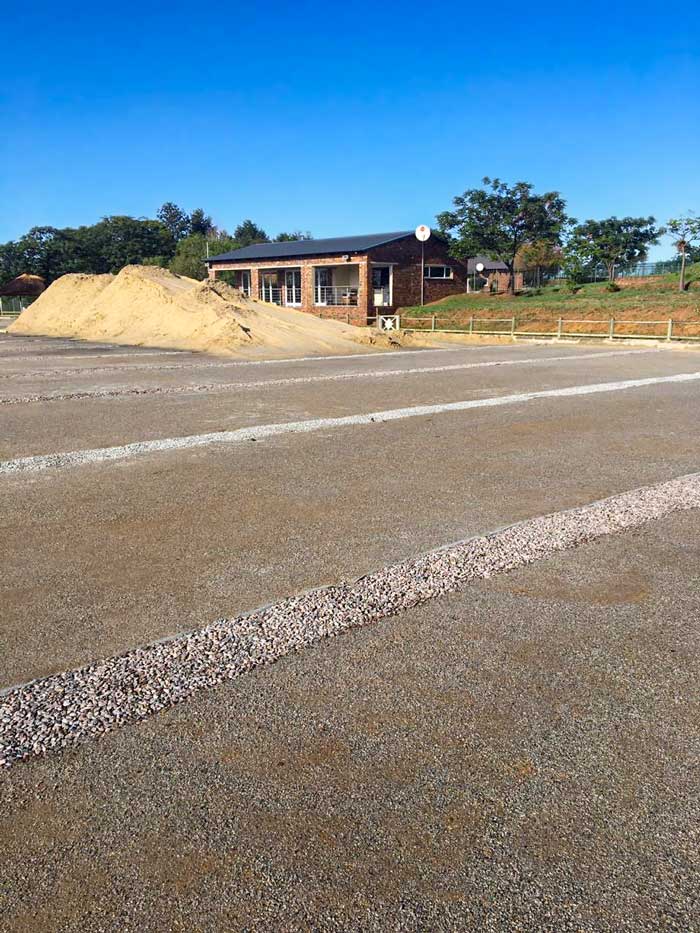

Out of our many past projects, one standout would have to be the track of a race course in Johannesburg, in South Africa.
In addition, TeMa supplies sustainable products like natural fibre matting — made from materials such as jute, straw, coconut and cellulose — that are particularly well suited to surface erosion control on grass slopes.
- Published in CORPORATION, Research and development, TeMa Technologies and Materials
TeMa at the 12th International Conference on Geosynthetics.
We too will be at the 12th edition of the International Conference on Geosynthetics that will take place in Rome, at the Parco della Musica auditorium from 17 to 21 September 2023, and which will involve a full programme of meetings between professionals (further information about the events here).
Four days of training and information meetings on geosynthetics, exploring all sub-types: woven and non-woven geotextiles, geogrids, geonets, geomats, drainage and reinforcement geocomposites, and geomembranes.
Geosynthetics are becoming increasingly popular in applications and fulfil various functions (often combined). For example:
- Drainage – drainage geocomposites and geonets.
- Filtration and Separation – woven geotextiles and non-woven geotextiles.
- Reinforcement – woven geotextiles and geogrids.
- Protection of waterproofing – studded membranes with truncated conical or star-shaped studs.
- Erosion control – geonets, geomats, biotextiles.
- Mechanical protection – non-woven geotextiles, composite geotextiles.
- Special applications – various geosynthetics made to specific requirements.
The main topics discussed will cover various fields of application, including anti-seismic design to road and railway embankments, erosion control, filtration and drainage functions, as well as an analysis of case studies.
The world of research is continuously evolving and the scheduled meetings will provide an excellent opportunity for sharing experiences and recent technical developments with engineers, geologists, consultants, contractors and whoever is involved in research and using geosynthetics.
During the exhibition event visitors will be able to take part in technical conferences, the Giroud lecture, special lectures and short courses , as well as visit the exhibition hall to meet manufacturers.
TeMa has thirty years of experience in using geosynthetics
The international event, entitled ‘Leading the way to a resilient planet’, fully represents the reason why TeMa began to manufacture and experiment with geosynthetics from the mid-1990s onwards: to research the most suitable technologies and materials for use in the construction of buildings and geotechnical works.
We have been involved in continuous interaction, also due to an increased awareness of major environmental issues. This has enabled us to broaden our range of products and expand in 80 countries worldwide.
Today, our catalogue includes many products that meet specific requirements for landfills, tunnels, road embankments, river banks and reinforced earth structures, gradually increasing performance for surface erosion control, rainwater drainage, and the reinforcement of grassy slopes.
The geosynthetics sector is rapidly developing and we are making huge investments, especially in research, so as to supply our customers with the best solutions, also tailor-made, for their projects. We share the same ‘urgency’ as our partners to pursue our unwavering ideal of respecting the environment and the hydrogeological protection of the land.
We look forward to seeing you in Rome from 17 to 21 September 2023, at Stand 22.
Meanwhile, you can discover all the details about the event here.
Reinforced earth retaining walls: specific products for each function
The function of retaining wall structures is to retain and reinforce soil faces. They can be built in a multitude of areas, including private ones such as gardens and vineyards, as well as public areas such as roads, railways and embankments.
They meet the need to recover usable spaces as they can also be built with a steeply sloping face.
The authentic green appearance
Nowadays, the modern building industry is highly aware of sustainability and territorial integration. Under certain conditions, reinforced earth retaining walls can replace conventional concrete walls, without underestimating the aesthetic appearance of the landscape. This is even more important in areas subject to landscape restrictions that require the preservation of natural aspects using specific materials and construction techniques.
TeMa Building solutions integrate these trends by catering to various problems concerning land conformation and hydrogeological protection.
The functions of reinforced earth retaining walls and the products required to achieve them
Slope gradient, exposure to weather conditions (including severe ones) and the mechanical properties of the terrain often require technical solutions that stabilise a slope. Synthetic products can be used, each one performing a specific function.
Reinforcement with geogrids
The compressive strength of the soil is combined with the tensile strength of the geosynthetic product (such as T-Grid). The friction involved develops a tensional state that stabilises the structure.
Profiling with formwork units
Electro-welded metal structures such as formwork units provide a shaping of the soil face up to a 65° slope.
Controlling surface erosion with erosion control mats
Severe or prolonged weather conditions, such as strong winds and sudden downpours – and the resulting surface run-off of water – could lead to erosion and depletion at the face of reinforced earth layers, particularly if they are fully greened. The solution to this problem is to use, on the face of each layer, three-dimensional synthetic mats such as T-Mat made of polypropylene or K-Mat FG Green made of fibreglass. Alternatively, natural, biodegradable mats made of jute fibre such as T-Juta 500 can be used (also available in an XLversion).
Soil containment using gabions
An alternative solution to reinforced earth walls can be found in walls built using double-twisted wire mesh gabions, such as T-Gabion, filled with pebbles. Gabions are also an interesting solution for smaller residential projects: they provide containment while offering a different and innovative aesthetic appearance.
- Published in BUILDING, Retaining walls, Retaining walls elements
Technical considerations in building reinforced soil walls
Reinforced soil walls have proved highly popular in recent years and are produced wherever possible, taking the place of concrete-faced soil retaining wall systems.
Employed in a range of different environments, they bring significant advantages, both financial and environmental. Indeed, unlike concrete-faced soil retaining wall systems, they:
- are sustainable because they give a vegetated finish;
- are a great space-saving solution, with slopes as steep as 80° (compared to the 30-40° of natural soil embankments);
- result in less pollution given the smaller number of trucks required to carry construction materials;
- make use of the excavated earth for backfilling, provided it is compatible with stability standards, meaning no more material needs to be brought in;
- blend seamlessly with their surroundings once the slopes are grassed over, without becoming a blot on the landscape of our villages.
Whatever the case, before planning the work, there are a number of aspects and data to be taken into consideration.
Preliminary data needed
To start with, all essential technical information must be procured in order to be able to assess the feasibility of the project, such as:
- geological testing of the area on which the wall is planned to be built
- topographical surveys
- meaningful cross-sectional drawings showing the current condition
- geometry of the planned wall (face angle, height, division into tiers, slope on top)
- external loads applied to the structure (top loads in the event it needs to accommodate a car park or a road)
- what earthquake risk zone the area is in
- geotechnical properties (angle of shearing resistance, cohesion and density) of the earth behind the future wall, of the foundation soil, and of the backfill
- whether there are perched aquifers or seepage of a different nature.
At this point, the next step is to check design calculations using specific software.
Checking design calculations
Checking is performed to assess both internal and external stability. The following tests are carried out in the former case:
- reinforcement strength test, which assesses possible failure mechanisms and determines the spacing, length and tensile strength of the geosynthetics due to be laid
- pull-out test to check that the reinforcement applied does not break or slide out
- direct sliding test, to ensure there is no translational movement across the installation planes
- wrap-around test, to ensure that the length wrapped around the top of each individual layer is stable.
The checks to be carried out during the project’s execution to assess external stability consist in sliding, overturning, bearing capacity and global failure analysis.
Do you want to chat with one of our experts to find the solution that best suits your requirements?
We have 30 years of experience in the industry and can give you access to materials and solutions offering specific performance. Contact us!
Do you want to learn more about the full TeMa Geo Solutions product range for reinforced earth structures? Click here.
Cycle and pedestrian paths: solutions to make them safer and more attractive.
Longer days, milder afternoons, a great desire to spend time outdoors and perhaps get some physical exercise, but also go to work and school or visit a friend… These are all good reasons for using, when available, cycle and pedestrian paths, possibly far from urban traffic.
The advantages of sustainable mobility
We are increasingly talking about environmental sustainability and the physical and psychological benefits of physical exercise:
- Less air and noise pollution caused by traffic.
- Reduced transport costs.
- Greater freedom of movement.
- Enhanced green areas in cities.
- Better quality of life by doing a bit of sport on a daily basis.
TeMa Geo Solutions for safety and urban benefits
‘Unequipped’ roads can be hazardous for those who choose to get around by bicycle: for this and environmental reasons, cycle and pedestrian paths are the ideal solution, as they are increasingly becoming part of local government mobility plans.
TeMa Geo Solutions offers all its experience by combining reinforced earth structures and their feature of being green, with cycle and pedestrian paths.
An embankment can be made or a road widened with its sides sloping at 65°/70° using the T-System (consisting of formworks, X-Grid PET geogrids and K-Mat FG Green erosion control mats as facing), thereby making the path safe and allowing a slope to turn green again. Making a slope green again provides a natural erosion control function: to encourage it, TeMa Geo Solutions recommends installing natural or synthetic mats. To make the structure stable, the T-System for reinforced soils adopted by TeMa involves using X-Grid PET geogrids.
Reinforced earth structures and drainage
For the extension works at the Serravalle Retail Park shopping centre in the Piedmont region, we helped the company choose the solutions to implement and assisted with verifications.
The area covering about 2,000 sqm required some intervention work regarding reinforced earth structures and drainage. In particular, we undertook the preliminary work for extension works dating back to 2016.
To the south-west of the building, the soil was secured and then surfaces were replanted with greenery.
Let’s see how this was done in more detail.
Type of intervention
In order to make the slope in front of the complex secure, the intervention work involved constructing reinforced earth structures in several banks, more specifically 3 modules of 6 m in height each.
In addition, to manage the water coming from the hydro-geographic basin situated upstream of the area, specific surface drainage works were carried out.
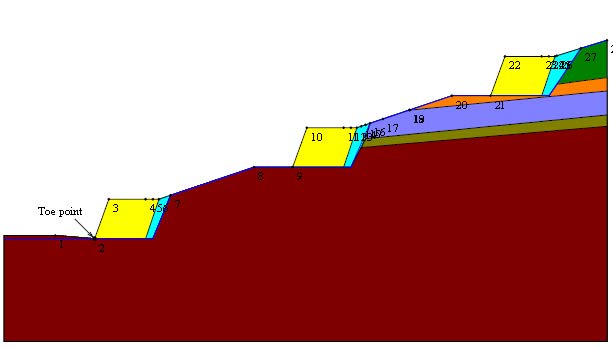
The solution from TeMa Geo Solutions
For the reinforced earth structure, 3 modules were constructed with anchorage lengths of 7 m and a strength of 110 kN/m provided by X-Grid PET PC 110 geogrids.
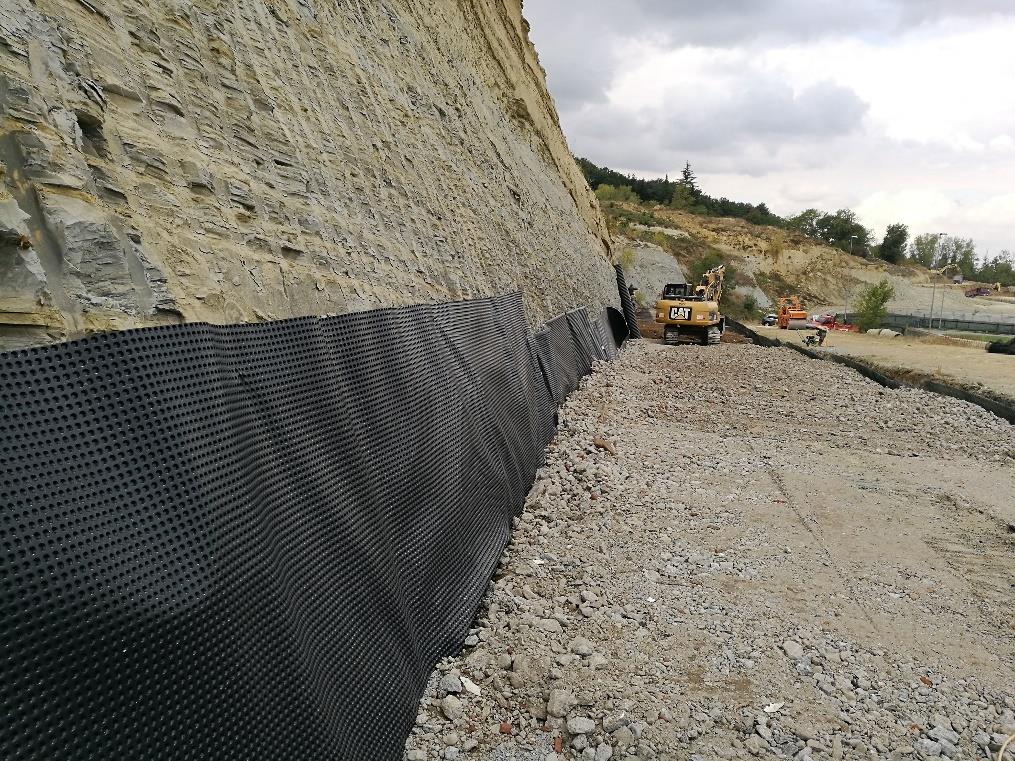
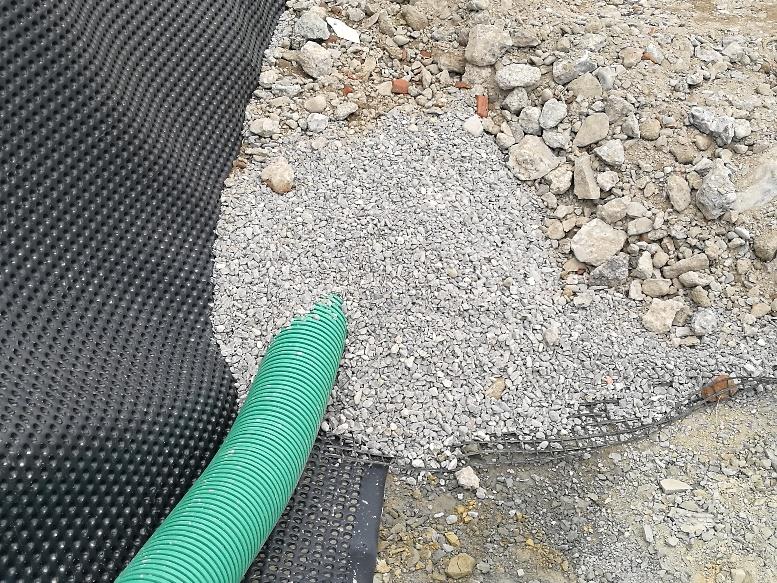
As for drainage, instead, a Membrana Nera Geo was used, the 8 mm HDPE studded membrane bonded to a filter nonwoven geotextile with a PE slotted tube at the base.
The drainage system was also installed at the horizontal contact points of each berm to prevent future water seepage into the reinforced earth structure.


Reinforced earth structures as noise barriers
Hearing the noise of traffic outside your window all day long is irritating and distracting and, in the long term, also harmful to your health.
This is why the WHO and a number of laws govern the use of noise remediation systems in cities: the Framework Law no. 447 of 1995 for Italy and the European Directive on Environmental Noise no. 49/2022. If the cause of the noise cannot be addressed, the solution is to install protective barriers. Various kinds can be used, but in this case we focus on reinforced earth structures that require specific measures, which we discuss here.
For example, the Pedemontana Veneta is a new toll motorway in Italy: nearly 100 km long. Almost entirely in operation in the north-east of the Veneto region, the main route of this motorway runs through a deep trench in order to minimise the ‘territorial’ and environmental impact on the surrounding area. This means that long sloping areas of reinforced earth can be found along the sides of the motorway, with rows of trees and hedges for 58.61 km and green areas covering 1,333,410 square metres of hedgerows, groves, grassy slopes and tree-lined meadows.
A focus on noise with much regard for the landscape.
What do reinforced earth noise barriers consist of?
For this type of embankment with its typical trapezoidal shape, earth is used that will be covered by vegetation over time. Geosynthetic reinforcements and geogrids are added to support the earth, which already has good compressive strength. These are inserted horizontally into the ground and develop friction and tension that stabilise the structure, increasing its resistance to stress.
The TeMa Geo Solutions offer includes the X-Grid Pet PVC range of geogrids, with different resistance values, which are ideal for all kinds of contexts.
Another aspect to bear in mind is surface erosion of the soil: to counteract this, synthetic geomats are applied, also with a mulching function to encourage the growth of grass cover, or natural fibre bionets.
Also in this case, TeMa Geo Solutions offers a wide choice ranging from Ecovermat F Grass and Ecovernet FJ to the K-Mat range.
Why use a vegetation barrier as a protective noise barrier?
A vegetation barrier has an unquestionable ability to limit the spread of sound waves: some of them are absorbed, some reflected and some deflected. As a result, the amount of sound waves reaching the receiver is greatly reduced and noise can be dampened by several decibels.
The advantages of a reinforced earth sound-deadening barriera
Creating reinforced earth structures brings considerable advantages:
- it costs less because you can often use earth available on-site
- no special maintenance is required other than regular trimming.
- it helps the environment and integrates with it: the use of vegetation also reduces vehicle emissions by absorbing CO 2 and purifying the air.
The importance of studded membranes
Research conducted in the building market has found that most construction disputes are due to damage caused by water and damp seeping into retaining structures.
Protecting foundations
In order to avoid inconveniences of this magnitude that are discovered in the course of time, designers and installers undertake to protect foundations. TeMa has therefore developed products and systems that protect waterproofing during backfilling operations, thus guaranteeing the stability of intervention work over time. For practical purposes, we propose two types of fairly common intervention works in civil engineering by showing you how two of our studded membranes work.
Retaining walls
Retaining walls are intervention works that have the main purpose of retaining slopes or soil embankments during works such as the construction of roads below ground level. Various types of wall can be built: in masonry or reinforced concrete, or using precast concrete elements.
Whichever solution is used, you always need to consider and comply with specific hydrogeological features: TeMa laboratories offer a range of membranes that meet such requirements, whereas technicians and installers can assist in choosing the best solution to use.
Mechanical protection of waterproofing
For the mechanical protection of waterproofing you can choose T-Kone, which also performs a damp-proofing and drainage function. Damp proofing creates a physical barrier between the structure and damp soil and avoids any possible damage to the waterproofing membrane, both during onsite operations and soil settlement.

The T-Kone family is part of a range of bare HDPE studded membranes (such as T-Kone S). Alternatively, these membranes can be bonded with a geotextile such as T-Kone G Drain or with a geotextile and a damp-proofing element such as T-Kone G Drain Plus.
Diaphragms and berlin walls
Suppose we need to work in an urban context doing underground intervention work. First of all, we must guarantee the stability of the structures surrounding the area to be excavated.
Diaphragms and berlin walls are used in situations where it is impossible to create excavation walls with an appropriate slope to prevent landslides or structural subsidence. In the form of steel/ reinforced concrete piles or walls, they are driven deep into the ground and coupled with TeMa membranes, which provide damp-proofing, mechanical protection or drainage functions.
Damp-proofing, mechanical protection or drainage functions
For this purpose, products such as Q-Drain can be used, which have a polypropylene monofilament drainage core bonded with one or two non-woven geotextiles, also made of polypropylene. These filter water and adapt to the conformation of the ground, thus guaranteeing stability.

These are just some of the membranes we are able to supply. Find out which one is best for you and assess the best solution with our team of experts. TeMa will assist you throughout each phase of the design process.
To discover TeMa products, visit the website.
- Published in BUILDING, Foundation and underground structures - Damp proofing systems, Foundation and underground structures - Drainage systems, Foundation and underground structures - Systems for mechanical protection, Foundation and underground structures - Systems for Waterproofing, Retaining walls, Retaining walls elements, Studded membranes and accessories










