TeMa at the 12th International Conference on Geosynthetics.
We too will be at the 12th edition of the International Conference on Geosynthetics that will take place in Rome, at the Parco della Musica auditorium from 17 to 21 September 2023, and which will involve a full programme of meetings between professionals (further information about the events here).
Four days of training and information meetings on geosynthetics, exploring all sub-types: woven and non-woven geotextiles, geogrids, geonets, geomats, drainage and reinforcement geocomposites, and geomembranes.
Geosynthetics are becoming increasingly popular in applications and fulfil various functions (often combined). For example:
- Drainage – drainage geocomposites and geonets.
- Filtration and Separation – woven geotextiles and non-woven geotextiles.
- Reinforcement – woven geotextiles and geogrids.
- Protection of waterproofing – studded membranes with truncated conical or star-shaped studs.
- Erosion control – geonets, geomats, biotextiles.
- Mechanical protection – non-woven geotextiles, composite geotextiles.
- Special applications – various geosynthetics made to specific requirements.
The main topics discussed will cover various fields of application, including anti-seismic design to road and railway embankments, erosion control, filtration and drainage functions, as well as an analysis of case studies.
The world of research is continuously evolving and the scheduled meetings will provide an excellent opportunity for sharing experiences and recent technical developments with engineers, geologists, consultants, contractors and whoever is involved in research and using geosynthetics.
During the exhibition event visitors will be able to take part in technical conferences, the Giroud lecture, special lectures and short courses , as well as visit the exhibition hall to meet manufacturers.
TeMa has thirty years of experience in using geosynthetics
The international event, entitled ‘Leading the way to a resilient planet’, fully represents the reason why TeMa began to manufacture and experiment with geosynthetics from the mid-1990s onwards: to research the most suitable technologies and materials for use in the construction of buildings and geotechnical works.
We have been involved in continuous interaction, also due to an increased awareness of major environmental issues. This has enabled us to broaden our range of products and expand in 80 countries worldwide.
Today, our catalogue includes many products that meet specific requirements for landfills, tunnels, road embankments, river banks and reinforced earth structures, gradually increasing performance for surface erosion control, rainwater drainage, and the reinforcement of grassy slopes.
The geosynthetics sector is rapidly developing and we are making huge investments, especially in research, so as to supply our customers with the best solutions, also tailor-made, for their projects. We share the same ‘urgency’ as our partners to pursue our unwavering ideal of respecting the environment and the hydrogeological protection of the land.
We look forward to seeing you in Rome from 17 to 21 September 2023, at Stand 22.
Meanwhile, you can discover all the details about the event here.
- Published in Drainage geocomposites and membranes, environmental, GEO, Geogrids, Reinforced earth structures - Drainage, Reinforced earth structures - Erosion control
Reinforcement of slopes and embankments
Slopes and embankments can be used as road or railway embankments, raised flood banks and floodplains, and even vineyards, especially in a territory such as Italy, one of the countries with the largest number of UNESCO World Heritage landscapes in the world.Many of those greened terraces are true reinforced earth structures, with their stability guaranteed by a well-tested construction technique.
Stability for slopes and embankments
Reinforced earth structures are retaining works that allow slopes and embankments to be supported, including steep slopes. They do not involve the use of concrete constructions, which would be more detrimental to the landscape.
The soil has a natural capacity for compressive strength. When combined with geosynthetic grids (which have excellent tensile strength), they create a stable system, as the features of the two components provide a high-performance composite.
The open mesh structure allows reinforcement geogrids to develop passive resistance along the transverse ribs, as well as creep resistance of the geosynthetic grid in relation to the soil. The TeMa Geo Solutions range includes X-Grid geogrids, available in a variety of models depending on the type of project.
How to position the geogrid in the layering of a terrain?
Each slope needs to be carefully and expertly engineered. However, in addition to the need to reinforce the raised earth structure with geogrids, it is essential to ensure surface erosion control using synthetic or natural erosion control mats and shaping with electro-welded wire mesh formwork.
The X-Grid geogrid must be applied to each ‘block’ of soil supported by the formwork, positioned between the backfill soil and the erosion control mat. An external wrap-around part, measuring no more than 150 cm, must be provided for the formwork system by installing formwork stiffening ribs approximately 30 cm apart.
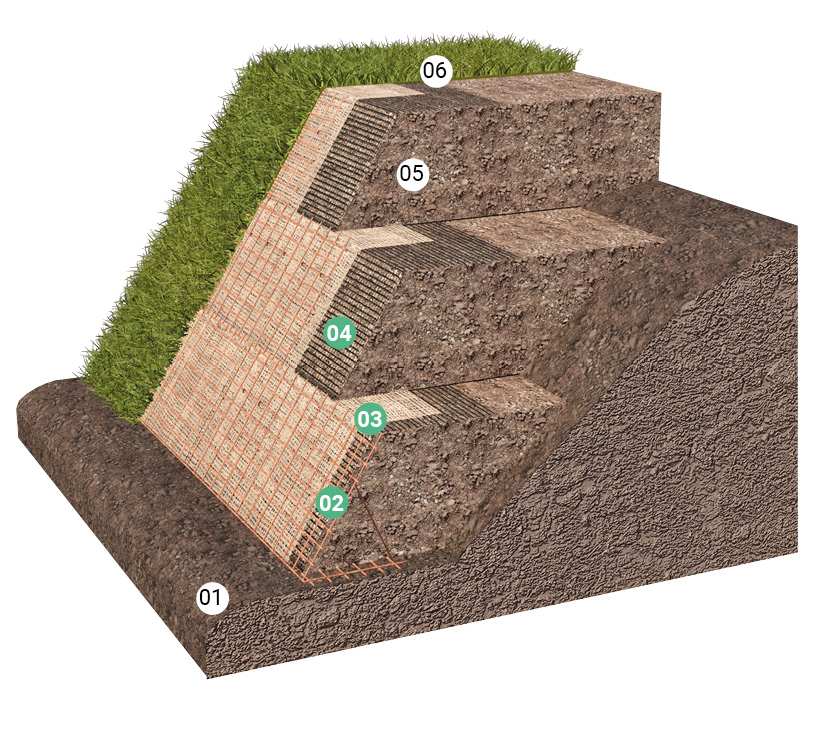
- Foundation soil
- Metal formwork
- Erosion control mat
- Geogrid
- Backfill soil
- Grassed surface
- Published in environmental, GEO, Geogrids, Reinforced earth structures
Controlling surface erosion with biomats and geomats
Soil erosion is an almost inevitable natural phenomenon that has become a greater concern in recent years due to the worsening climate situation – in Italy, for example, 132 extreme weather events were recorded between January and July 2022, a higher number than the annual average over the last decade – combined with long periods of drought.
Strong winds, heavy rain, hail and runoff tend to remove the surface layer of exposed soils, which often include organic matter and seeds. Climate change facilitates erosion, making it not only inevitable but also hazardous if left uncontrolled.
It’s essential to counter or mitigate the phenomenon: soil provides us with food, biomass and raw materials; human activities take place on it and it’s part of the landscape and our cultural heritage.
Which structures are more subject to surface erosion?
The areas of application most affected by the erosive action of the climate are:
- slopes and the sides of landfills and contaminated sites, and those that have been grassed for appreciable aesthetic improvement;
- reinforced earth structures, more specifically terracing in vineyards and the embankments of canals or rivers;
- ascending/descending ramps from flyovers, tunnel entrances and noise barriers on roads and railways;
- dry, rocky slopes, of all angles, that shape the terrain of Italy.
The effects of surface erosion
The uncontrolled removal of the surface topsoil and the failure of vegetation to take root results in ‘thinning’ of the soil and a risk to the stability of sloping areas.
What can be done to prevent surface erosion?
We should begin by pointing out that a case-by-case assessment is required that considers many variables, such as the nature and uniformity of the soil, the slope gradient, the type of slope (dry or rocky) and the weather conditions in the area where intervention work is to be carried out.
In general, vegetation, whatever type it is, has a natural ability to protect soils from erosion. So the best course of action is to quickly encourage grassing and then apply biodegradable mats made of jute, straw, coconut and cellulose fibre, which can also be pre-seeded.
TeMa Geo Solutions recommends biomats such as Ecovermat, Ecovermat P and PC, and Ecovernet.
Alternatively, or combined with these, synthetic geomats, mainly made of polymer monofilaments, can be used.
Once laid, they are covered with another layer of soil: in this way, the roots of growing vegetation will become entangled with the geomat, creating an almost permanent erosion protection system.
Once again, TeMa Geo Solutions offers a wide range of geomats to choose from.

Uncertain about what to choose? We can help you. CONTACT US!
TeMa even more transparent about sustainability
With the new EPD certification, TeMa Technologies and Materials provides information about the level of sustainability of its products: this includes most of the membranes and geocomposites manufactured on its production lines. For 30 years, TeMa has regarded environmental protection as a duty and obligation towards the community and future generations.
What is EPD and what is analysed to obtain it?
The Environmental Product Declaration (EPD) is a document that provides specific data on the life cycle of products or a service. It measures the impacts that the production and life phases of a product have on the environment by means of a Life Cycle Assessment to determine the consumption of resources such as water, materials and energy.
It is voluntary and verified by the independent third party SGS so that certified declarations can be given to clients.
International acknowledgement
The EPD document is internationally acknowledged, as it complies with ISO standards. This ensures use, credibility and stability over time, making the data collected available for use in any type of environmental management system and providing information for environmental certification protocols for buildings and infrastructures.
Which product lines from TeMa Building Solutions are EPD certified?
The products having obtained EPD certification are:
- the studded membrane line, which includes Membrana Nera, Membrana Nera Geo, T-Kone, Tefond, HDD, TM and MD;
- the monofilament drainage line comprising Q-Drain C and Q-Drain ZW;
- the anti-erosion and reinforcement geomat line, which includes K-Mat and X-Grid AM.

Our certificates can always be consulted by clicking here and entering TeMa in the filters.
- Published in CORPORATION, news, TeMa Technologies and Materials





