Protecting outdoor flooring with drainage geocomposites
Autumn precipitation, winter frosts and scorching summer heat may even be followed by a downpour lasting a few minutes. Terraces and balconies, or outdoor flooring in general, are affected by seasonal and sometimes daily weather events and temperature fluctuations that put the resistance of flooring at risk.
So how can we protect them?
Drainage geocomposites are the solution, but let’s take a closer look at them and their functions.
What are drainage geocomposites and when should they be used?
They are geosynthetic materials with a drainage core bonded to a non-woven filtering fabric. They can be used on walls, underground structures, flat roofs, trafficable roofs, flat green roofs, as well as terraces, balconies and outdoor flooring.
TeMa Interior Solutions suggestsT-K NW and T-K Net, polyethylene studded membranes bonded to a non-woven fabric that acts as a filtering layer for T-K NW or a HDPE mesh for T-K Net.
What are the functions?
The functions of geosynthetic products are set out in the UNI EN ISO 10318 standard.
![]()
Drainage
As the name implies, the main function of geosynthetic products is to drain any water that may seep into the screed. Passive capillary drainage eliminates the risk of stagnant water in the system and, if there are rooms below, prevents moisture from damaging the insulating layer.
![]()
Protecting the waterproofing layer
Damage to the waterproofing layer causes significant and immediately visible problems. Moisture and water penetrating into deeper layers, compromise the durability and strength of the structure, causing cracks in tiles. Protection is therefore necessary.
![]()
Distributing the load
Flooring often has to withstand heavy loads, such as outdoor tables, sunshades, large plant pots etc…. Using studded membranes, which are highly resistant to loads, allows the screed to remain “suspended” from the sealing layer (i.e. the waterproofing layer) below, protecting it from perforations and abrasions.
Advantages of applying the system
The time required is extremely short and flooring can be laid after a few days.
The thickness of the membranes is much reduced, an advantage not to be underestimated in renovations. Moreover, the thresholds of French windows opening outwards or onto a terrace do not need to be raised.
Lastly, in consideration of the environment, the materials are safe and odourless. They do not develop toxic gases or organic components, and comply with VOC standards. No hazardous substances are released underground.
- Published in Balconies and terraces, INTERIOR, Levelling, or structural, waterproofing panels, Waterproofing system with membranes, Waterproofing with panels
New solutions in road construction and/or repairs
The safety of road infrastructures is the main goal, and maintenance work – whether preventive or supplementary – is systematic.
Road surfaces withstand heavy traffic loads and atmospheric changes with significant variations in temperature. Constant maintenance is therefore required in order to ensure even surfaces and the stability of structural elements.
Let’s look at the main factors involved in building new roads or maintaining roads.
Controlling surface erosion
Erosion is largely due to freeze/thaw cycles, which make asphalt less elastic and therefore more prone to internal voids. Such voids allow water to penetrate into underlying layers, gradually eroding the structure.
In addition, heavy traffic loads, especially heavy vehicles, cause deformation of the surface layers: this results in water penetration, which “softens” the structure and makes it less resistant.
Anti-capillary drainage
The water capillarity, i.e. the ability of liquids to move in micro-spaces even against the force of gravity, is a rather complex concept closely monitored in the construction industry. With the help of pressures exerted on lower layers, water rises upwards, dragging the finer components of materials with it and causing deformation.
It is therefore necessary to provide a drainage geocomposite, a three-dimensional membrane obtained by bonding two or more synthetic components in order to convey fluids to the exterior and prevent them from rising.
You can discover all our solutions here.
Reinforcement
It may sometimes be necessary to install reinforcement grids, especially if there is a more or less pronounced slope that would cause a road shoulder to slide downwards.
The choice of the most suitable type of reinforcement, and therefore also of the position of the geogrid in the layering, clearly depends on the problems to be faced i.e. reinforcing the surface area to limit the spread of cracks to underlying layers, improving the load-bearing capacity and reducing the stresses transmitted to lower layers, or providing a separation (and anti-contamination) function.
Discover all our solutions here.
Stabilisation
During intervention works, softer soils may be encountered, which may be subject to instability or even collapse in the early stages of intervention works. Even if this should not jeopardise the feasibility of the works, there is still the risk that the minimum legal safety requirements will be compromised.
Also in this case, geosynthetic products are the solution to the problem, as they absorb tensions at least until the intervention work achieves structural stability.
Discover the solutions in the X-Grid line here.
- Published in Drainage geocomposites and membranes, Erosion mats, GEO, Geogrids, Roads
Why don’t puddles form on soccer fields?
Let’s take a step back: nowadays, synthetic turf fields are the most cost-effective solution for football clubs, for both the first team and the youth sector. So, the construction of a synthetic system is an opportunity not to be missed. It is therefore important to construct a synthetic field that is ideal for the type of use and level of play.
TeMa staff can assist in the construction – especially in the design phase – to define the characteristics of the synthetic turf field. We are very familiar with the different layers it is made of (sub-base, turf and sand, rubber or natural infill) and its various features recommended by experience depending on different climatic conditions. The initial step is also important for determining the procedure that any club – in almost all cases through the municipality, the owner – needs to follow in order to construct the most suitable synthetic field in terms of type and frequency of use.
The secret is…
…drainage. Having a quality sub-base is even more important than the surface turf. This is where the experience of TeMa steps in with the company’s drainage solutions, developed on 4 continents. They guarantee the timely disposal of water in the quickest possible time and the use of the field even in severe weather conditions.
Drainage of a synthetic turf field
On synthetic turf fields water drainage is horizontal: after stabilising and levelling the surface, an impermeable membrane is applied that prevents liquids from penetrating into the ground below, conveying them to the channels on the long sides of the field.
This prevents water from stagnating on the surface of the field, avoiding puddles and the removal of surface material.
Natural or synthetic turf for the field?
A natural grass surface requires more maintenance and higher costs: it needs to be cut at regular intervals, treated, fertilised and watered. Moreover, weather conditions may affect the use of the field.
By contrast, synthetic turf is more resistant to weather conditions. It can also be used intensively all the time, regardless of the season and requires much less maintenance: it only needs to be “combed” regularly to revitalise the turf.
In addition to the (much) shorter construction time, a factor that tends to make synthetic turf preferable to natural turf is its permeable capacity: the control over water filtration is clearly superior and the sub-base is designed to drain excess water during heavy rainfall and/or store it. This makes it easier to maintain favourable conditions for both the game and the durability of the field, while also protecting the health of the players.
What makes the field so even and linear?
Drainage geocomposites provide maximum performance.
Q-Drain ZW8 Football consists of a monofilament core bonded with two non-woven fabrics, to which a PE membrane can be added if required.
Q-Drain ZW8 WP Football, ideal for horizontal drainage applications, consists of a monofilament core bonded with a non-woven fabric and a waterproofing film.
To support these products, we recommend T-Kanal Football, a cement channel for perimeter drainage that contains a special drainage membrane. The system is made complete with a grid, fixings and T-Tape, for joining the rolls during installation.
- Published in GEO, Synthetic turf soccer fields - Accessories
Can’t go up? Let’s make space below!
Nowadays, certain solutions allow you to create perfectly liveable and comfortable basements.
Of course, existing little-used basements can also be renovated, but you need to take some constructive measures to ensure that the building is in good condition and the environment is healthy.
So let’s see what we need to focus on.
Damp and moisture seepage
Basements are in direct contact with the ground, both the floor and the vertical walls.
Rainwater or ground moisture can penetrate concrete, leading to marks and mould that may cause the wall to peel. The aesthetic damage is as serious as the structural damage: mould is anything but healthy!
It therefore becomes necessary to provide a separation barrier between the structure and the ground that performs the function of damp-proofing, i.e. controlling moisture in the absence of hydrostatic pressure (click here to read more).
TeMa Building Solutions suggests T-Bentostop, in the F and F XL versions, a geocomposite, which attaches to concrete and consists of natural sodium bentonite with a waterproofing function, and T-Kone, the HDPE studded membrane available in several versions.
![]()
Drainage
Groundwater or dispersed water may flow in the ground, even near structures, therefore increasing the load on walls. So, it is essential to drain water and prevent it from entering by reducing the hydrostatic pressure on surfaces: T-Kone G Drain, T-Net Drain studded membranes and the drainage geocomposites in the T-Mix Drain range perform this function while keeping walls dry.
![]()
Mechanical protection of waterproofing
The vertical walls of basement rooms have to withstand heavy loads exerted by the ground. It is therefore essential to provide systems to protect the waterproof layer in order to guarantee the safety and long life of the building.
The T-Kone, T-Kone Star and TMD (also in the Plus version) range are studded membranes specifically designed for foundations and underground structures: their high load-bearing capacity makes them ideal for such applications.
![]()
Aeration
To keep masonry dry and allow constant and substantial air circulation, studded membranes can be installed with the studs facing inwards. In this way, their raised shape creates aeration channels that allow the wall to literally “breathe”.
Ideas for renovating your basement
It has been estimated that the value of your property increases by about a third if you have a well-planned basement. An extra room is always very useful and its intended use may vary greatly.
You can opt for a studio for working from home, a spacious laundry room for hanging up your washing, a playroom for your children, a relaxation area, a rehearsal room for talented home musicians, or even a free space for hosting friends, a wine cellar for preserving the best bottles with a tasting area, a gym or a personal home cinema.
- Published in BUILDING, Drainage geocomposites, Foundation and underground structures, Foundation and underground structures - Damp proofing systems, Foundation and underground structures - Drainage systems, Foundation and underground structures - Systems for mechanical protection, Foundation and underground structures - Systems for Waterproofing, Studded membranes and accessories
The importance of guaranteeing protected foundations
Cloudbursts are sudden heavy rainstorms that, unfortunately, are becoming increasingly frequent. Short but intense, they mainly occur in the summer season, even if it is a myth to debunk because they are also a common occurrence in other seasons. The enormous amount of water concentrated over a short period of time, makes these phenomena potentially dangerous and a possible threat to the foundations of buildings.
How to Protect Foundations
This is why designers are increasingly focusing on the best protection for buildings and properties in contact with the ground. The sudden changes in the amount of water run-off and the gradual increase in the groundwater level make earth-retaining works fragile when these factors have not been considered.
TeMa Building Solutions
Adequate systemic design is essential in the case of hydrostatic thrust, just as it becomes fundamental to monitor various factors, including: descending water resulting from precipitation, water and/or damp rising due to capillary upward flow, groundwater and condensation which, due to the difference in temperature between the ground and interior spaces, forms on the walls of rooms close to the ground. It’s also important to bear in mind the likelihood that several phenomena may exist at the same time. TeMa Building Solutions is our division highly specialised in protection and waterproofing systems. Our research team has developed products ideal for counteracting the hazards caused by these seasonal weather events. It provides solutions for the protection of foundations and water drainage to reduce the volume of water close to underground structures, both vertical and horizontal, in contact with the ground and where groundwater or dispersed water is present.
TeMa Geocomposites
Our geocomposites have been designed to perform the dual function of filtering and draining water, dispersing energy from the hydrostatic load. They include T-Net Drain 5, which channels the flow of water to the water collection system around a building thanks to the rhomboidal-shaped mesh geo-grid coupled with two non-woven geotextiles.
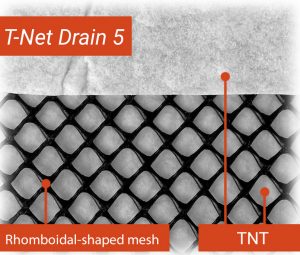
According to recent research in the building market in Italy, damage due to water seepage and damp in earth-retaining structures is the cause of more than 50% of disputes in the building sector. Our designers are well aware of this problem and therefore rely on TeMa, thus preventing such complications.
To learn more and discover the entire range of geocomposites designed by TeMa, go to our website.
The importance of studded membranes
Research conducted in the building market has found that most construction disputes are due to damage caused by water and damp seeping into retaining structures.
Protecting foundations
In order to avoid inconveniences of this magnitude that are discovered in the course of time, designers and installers undertake to protect foundations. TeMa has therefore developed products and systems that protect waterproofing during backfilling operations, thus guaranteeing the stability of intervention work over time. For practical purposes, we propose two types of fairly common intervention works in civil engineering by showing you how two of our studded membranes work.
Retaining walls
Retaining walls are intervention works that have the main purpose of retaining slopes or soil embankments during works such as the construction of roads below ground level. Various types of wall can be built: in masonry or reinforced concrete, or using precast concrete elements.
Whichever solution is used, you always need to consider and comply with specific hydrogeological features: TeMa laboratories offer a range of membranes that meet such requirements, whereas technicians and installers can assist in choosing the best solution to use.
Mechanical protection of waterproofing
For the mechanical protection of waterproofing you can choose T-Kone, which also performs a damp-proofing and drainage function. Damp proofing creates a physical barrier between the structure and damp soil and avoids any possible damage to the waterproofing membrane, both during onsite operations and soil settlement.

The T-Kone family is part of a range of bare HDPE studded membranes (such as T-Kone S). Alternatively, these membranes can be bonded with a geotextile such as T-Kone G Drain or with a geotextile and a damp-proofing element such as T-Kone G Drain Plus.
Diaphragms and berlin walls
Suppose we need to work in an urban context doing underground intervention work. First of all, we must guarantee the stability of the structures surrounding the area to be excavated.
Diaphragms and berlin walls are used in situations where it is impossible to create excavation walls with an appropriate slope to prevent landslides or structural subsidence. In the form of steel/ reinforced concrete piles or walls, they are driven deep into the ground and coupled with TeMa membranes, which provide damp-proofing, mechanical protection or drainage functions.
Damp-proofing, mechanical protection or drainage functions
For this purpose, products such as Q-Drain can be used, which have a polypropylene monofilament drainage core bonded with one or two non-woven geotextiles, also made of polypropylene. These filter water and adapt to the conformation of the ground, thus guaranteeing stability.

These are just some of the membranes we are able to supply. Find out which one is best for you and assess the best solution with our team of experts. TeMa will assist you throughout each phase of the design process.
To discover TeMa products, visit the website.
- Published in BUILDING, Foundation and underground structures - Damp proofing systems, Foundation and underground structures - Drainage systems, Foundation and underground structures - Systems for mechanical protection, Foundation and underground structures - Systems for Waterproofing, Retaining walls, Retaining walls elements, Studded membranes and accessories
- 1
- 2







