TeMa Geo Solutions: geotechnical solutions
The TeMa Geo Solutions division has developed considerable experience in geotechnical applications and developed technologies and products, thereby ensuring that designers can meet increasingly strict regulations concerning the environment and the landscape.
These applications are for the protection, maintenance, retention, reinforcement and drainage in the field of major environmental projects, involving products that provide innovative efficient and long-lasting solutions.
We are aware that a kind of public resistance to sustainability announcements has already begun. We are therefore interested in helping companies that are taking appropriate action to protect the environment. This is not only to ensure that they can better comply with regulations but also, and above all, to increase the effectiveness and credibility of their work.
TeMa Geo solutions in applications
The areas of expertise of TeMa Geo Solutions include:
- football fields
- landfills and contaminated sites
- tunnels
- reinforced soil retaining structures
- dry slopes
- grassy road and railway embankments
- roads
- drainage ditches
- horse training and racing tracks.
Products and functions: a range starting with geosynthetics
Geogrids are structural elements used to reinforce soils in the construction of retaining walls, block retaining walls, reinforced soil retaining structures, landfills and contaminated sites. The open mesh structure allows the reinforcement geogrids to develop ‘passive’ resistance at the transverse ribs, thus effectively increasing their inherent stabilising effect and enabling the system to withstand significant levels of stress.
The TeMa Geo Solutions range includes uniaxial or biaxial X-Grid geogrids made of fibreglass, polyester or PET coated with a polymer layer, coupled, or not, with a nonwoven geotextile, to be chosen to suit the project.
Offering products such as bentonite geocomposites, drainage geocomposites, facings, erosion control mats and essential accessories, the TeMa Geo Solutions range fulfils various functions for the retention anddrainage of rainwater and groundwater.
The TeMa Geo world offers its long-standing (since 1993) expertise and experience in the polymer-based product category (geosynthetics). Over the years, research at its in-house labs has enabled the development of solutions that integrate with the environment in a more specific sense, such as biodegradable erosion control mats, and in a broader sense, such as geomats and studded membranes.
TeMa also offers cutting-edge geotechnical solutions for vineyards
This is not surprising, as the TeMa Geo headquarters are situated on the eastern edge of the Prosecco hills, a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The company therefore has made its experience available to preserve and protect the viticultural landscape with its products for erosion control, reinforcement and ground drainage in an environment subject to the passage of agricultural vehicles. Click here to download the specific catalogue.
- Published in Drainage geocomposites and membranes, Erosion mats, GEO, Geogrids, Landfills, Reinforced earth structures, Roads, Synthetic turf soccer fields - Accessories, Tunnels
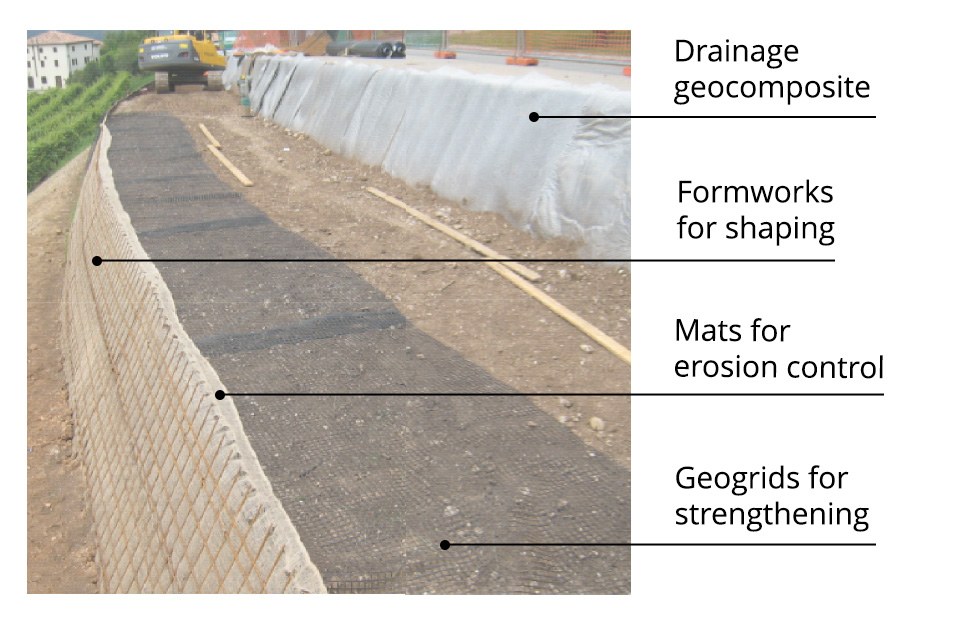
System for reinforced soil retaining structures
T-System is the system from TeMa Geo Solutions that includes various components for strengthening, surface erosion control, drainage and retaining used in the construction of reinforced soil retaining structures: innovation that we’ve been exploring here at TeMa since our inception 30 years ago, and that is now one of our hallmarks. Let’s take a more detailed look below.
Components for strengthening
Designed for strengthening, the knitted X-Grid PET C geogrids are made from high-strength polyester yarn, with a protective polymer coating. They deliver tensile strength in the 20 kN/m to 800 kN/m range.
Components for erosion control
They protect the face of the structure from erosive agents, like wind and driving rain, until the vegetation has had time to establish. TeMa Geo Solutions offers natural solutions made from cellulose fibres, like Ecovermat, or jute fibres, like Ecovernet, as well as synthetic solutions made from monofilaments (K-Mat F), polypropylene (K-Mat FA) or fibreglass (K-Mat FG Green).
Components for drainage
Drainage geocomposites like Q-Drain are used to address the problem of water seeping into the backfill.
Components for retaining
We have a line of facings made from electrically welded wire mesh — with inclinations ranging from 65° to 80° — to ensure the exposed face is straight.
Practical tips
On site
System components must be stored well away from machinery, and suitably protected from dust or residues from work on site.
To avoid excessive overlaps and waste, the X-Grid geogrids must be cut to size using a suitable metal stand with metal trestles supporting a circular rod to be inserted inside the roll.
Erosion control components — whether biodegradable or synthetic — must be stored in a dry place and not in direct contact with the natural ground, so as to avoid laying problems later on.
Metal formwork must be stored well away from areas where machinery is operating, and carried in only when it is time to install.
During assembly, it is best to apply U-shaped strips of rubber or metal so that the geogrids can be wrapped correctly over the formwork without getting caught on the top of the bars. (see photo)
Special instructions
We advise against backfilling with silty and clayey material; at the very least, only use this kind of material after mixing it with aggregate.
The full range of system components comes with instructions on the relevant procedures to be followed. Contact us, we’ll be happy to provide case studies and full information.
Safety first: and that applies to landfills, too
TeMa Geo Solutions’ thirty years of experience extends to the field of controlled landfills and contaminated sites, with products specially designed for each function to ensure the site is safe, and with investment-conscious solutions, as well as a focus on ensuring peak performance.
Safe landfills legislation
In Italy, regulation around the controlled disposal of waste dates back as far as 1982, later supplemented by the European directive and updated in 2020 by Italian legislation (D.Lgs no.121).
This legislation covers all aspects of the disposal cycle, from landfill classification to the type of waste, as well as criteria for the construction and operation of the facilities, with a strong environmental focus. In this regard, TeMa has come up with built-up systems and materials that fulfil the required functions and comply with the relevant legislation.
The main functions to make safe a controlled landfill
Making safe a landfill facility entails fulfilling a number of functions:
![]() Barrier
Barrier
Walls and floor must be isolated to protect groundwater and soil from leachate and biogases resulting from decomposition processes. To ensure sufficient watertightness, legislation requires the use of at least 0.5 m of clay or, drawing on the principle of hydraulic equivalence, synthetic products: sodium bentonite composites like Barrier Bento — which contains up to 5 kg of bentonite/sqm sandwiched between two geotextiles — provide an impermeable layer, acting as a barrier between soil and waste.
![]() Reinforcement
Reinforcement
One of the major issues to be addressed when designing landfills, especially the capping system, is stability, which can be achieved by leveraging the compressive strength of the soil combined with the tensile strength of geosynthetics. Reinforcement solutions provided by TeMa range from PET-series geogrids to geomats laminated with geogrids.
![]() Drainage
Drainage
For liquid and gas capture, legislation calls for the use of 50 cm of aggregate, which nonetheless can come with its own stability issues, especially on steeper slopes. With the use of drainage geocomposites, the relevant built-up system can be pared back, while the number of vehicles required to carry materials can also be reduced. TeMa’s offering ranges from studded and micro-studded membranes to monofilaments laminated with nonwovens, and geonets with one or two nonwoven layers.
![]() Erosion control
Erosion control
The top layer of the soil is eroded by the action of the elements — especially by the type of unpredictable and extremely violent weather events we’ve witnessed in recent years — triggering alarming landslips, which can undermine a site’s hydrogeology. To prevent issues of this kind, it’s essential to encourage vegetation (which serves as a form of natural erosion control) and protect the soil while it takes root by using natural or synthetic mats from TeMa.
Ballasted roofs: why gravel, and how to protect their waterproofing
Something of an innovation in the Italian building scene, while also being a useful device for protecting the roof, the ballasted flat roof is a solution that can become a distinctive feature of either a residential or commercial building.
Unlike the traditional system involving the use of concrete, using gravel is an option that brings a number of attractive advantages:
- it protects the roof against wind and UV rays
- it protects the roof against mechanical damage
- it is low maintenance
- it provides thermal comfort in summer as it shades the roof
- it makes the whole roof system practically fireproof
- it is long lasting.
In building, the choice of a ballasted roof is often prompted by aesthetic reasons for a holiday home or a hotel by the sea, or in an area with high sunshine hours… while it also caters to the need for optimal insulation and low maintenance.
The TeMa Building Solutions answer for protecting ballasted roofs
When gravel is laid, the load can tear the waterproofing layer on the roof underneath, and this comes with the risk of leaks, with all the ensuing stain, mould and structural damage issues.
So it is important to address the need for rainwater drainage and mechanical protection of the waterproofing.
TeMa Building Solutions has come up with a product that serves multiple functions: the product in question is T-Kone G Drain, the studded membrane (which serves to protect the waterproofing) featuring a geotextile (addressing the need for filtration and separation).
Placed between the gravel layer and waterproofing, T-Kone G-Drain is thin, strong and ideal for an effective build-up without the bulk.
- Published in Ballasted roofs, BUILDING, Studded membranes and accessories
Technical considerations in building reinforced soil walls
Reinforced soil walls have proved highly popular in recent years and are produced wherever possible, taking the place of concrete-faced soil retaining wall systems.
Employed in a range of different environments, they bring significant advantages, both financial and environmental. Indeed, unlike concrete-faced soil retaining wall systems, they:
- are sustainable because they give a vegetated finish;
- are a great space-saving solution, with slopes as steep as 80° (compared to the 30-40° of natural soil embankments);
- result in less pollution given the smaller number of trucks required to carry construction materials;
- make use of the excavated earth for backfilling, provided it is compatible with stability standards, meaning no more material needs to be brought in;
- blend seamlessly with their surroundings once the slopes are grassed over, without becoming a blot on the landscape of our villages.
Whatever the case, before planning the work, there are a number of aspects and data to be taken into consideration.
Preliminary data needed
To start with, all essential technical information must be procured in order to be able to assess the feasibility of the project, such as:
- geological testing of the area on which the wall is planned to be built
- topographical surveys
- meaningful cross-sectional drawings showing the current condition
- geometry of the planned wall (face angle, height, division into tiers, slope on top)
- external loads applied to the structure (top loads in the event it needs to accommodate a car park or a road)
- what earthquake risk zone the area is in
- geotechnical properties (angle of shearing resistance, cohesion and density) of the earth behind the future wall, of the foundation soil, and of the backfill
- whether there are perched aquifers or seepage of a different nature.
At this point, the next step is to check design calculations using specific software.
Checking design calculations
Checking is performed to assess both internal and external stability. The following tests are carried out in the former case:
- reinforcement strength test, which assesses possible failure mechanisms and determines the spacing, length and tensile strength of the geosynthetics due to be laid
- pull-out test to check that the reinforcement applied does not break or slide out
- direct sliding test, to ensure there is no translational movement across the installation planes
- wrap-around test, to ensure that the length wrapped around the top of each individual layer is stable.
The checks to be carried out during the project’s execution to assess external stability consist in sliding, overturning, bearing capacity and global failure analysis.
Do you want to chat with one of our experts to find the solution that best suits your requirements?
We have 30 years of experience in the industry and can give you access to materials and solutions offering specific performance. Contact us!
Do you want to learn more about the full TeMa Geo Solutions product range for reinforced earth structures? Click here.
Tips for the correct laying of TMD 1011
For vertical applications, such as foundation walls, and for horizontal applications, such as flat roofs, mechanical protection of waterproofing is required and, often, also drainage: TMD 1011 is a studded membrane, produced by TeMa Building Solutions, that performs both functions: drainage for vertical applications and waterproofing protection for horizontal applications.
A few tips for laying TMD 1011 on horizontal surfaces
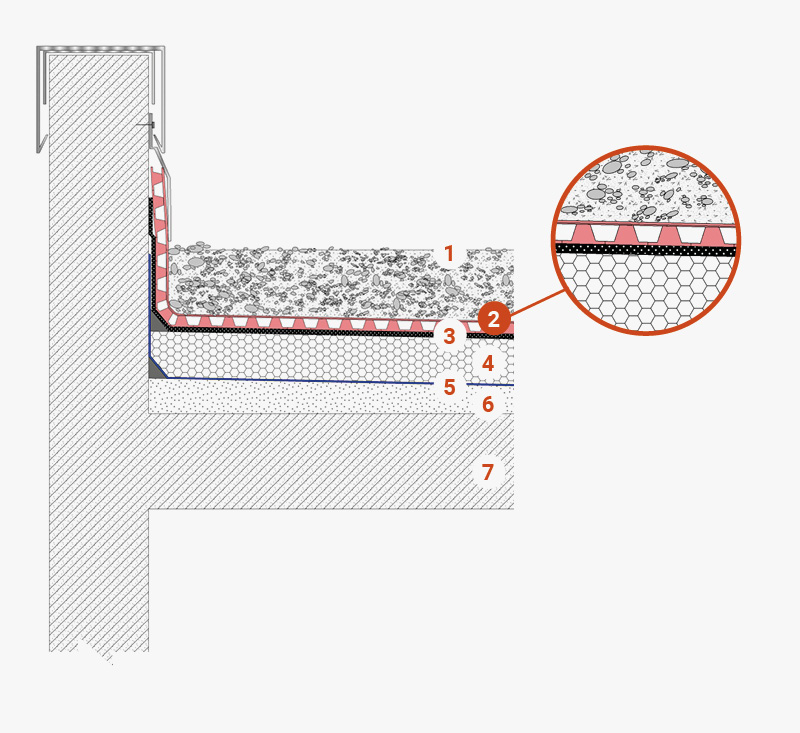
Flat roof with gravel finish (weighted)
1 Gravel finish
2 TMD 1011 membrane serving as a drainage layer and for waterproofing protection
3 Waterproofing membrane
4 Thermal and acoustic insulation
5 Vapour barrier
6 Sloping underlayment
7 Load-bearing structure
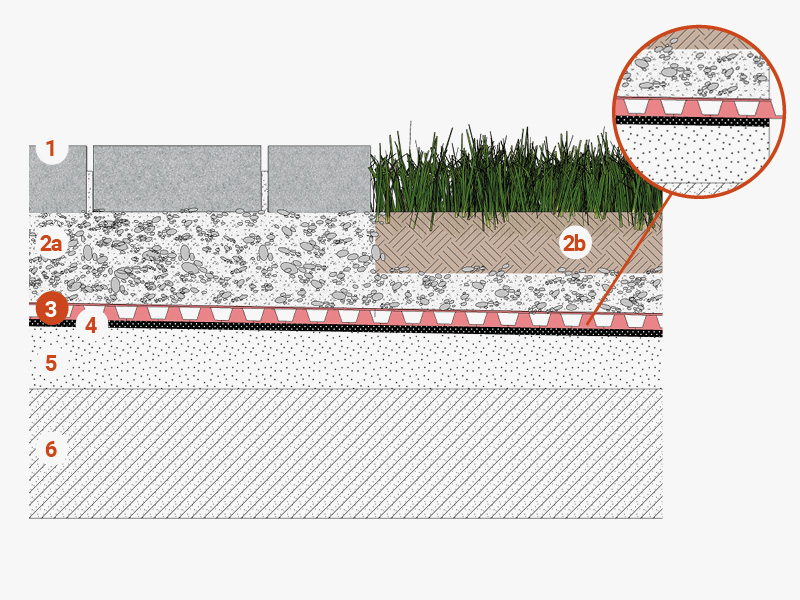 Walkways and green areas
Walkways and green areas
1 Interlocking block paving
2a Crushed stone bedding course
2b Growing medium
3 TMD 1011 membrane serving as a drainage layer and for waterproofing protection
4 Waterproofing membrane
5 Vapour barrier
6 Sloping underlayment
7 Load-bearing structure
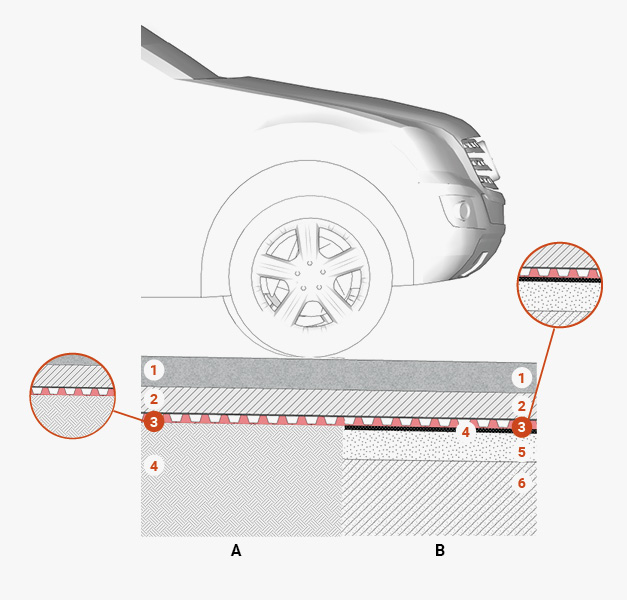
Surfaces suitable for vehicle traffic A
1 Paving designed to take vehicle loads
2 Sand bedding layer
3 TMD 1011 membrane serving as a:
– drainage layer
– substrate in place of traditional concrete levelling compounds
– separating and leachate containment layer (oils or hydrocarbons)
4 Substructure / ground
Surfaces suitable for vehicle traffic B
1 Paving designed to take vehicle loads
2 Sand bedding layer
3 TMD 1011 membrane serving as a drainage layer and for waterproofing protection
4 Waterproofing membrane
5 Sloping underlayment
6 Load-bearing structure
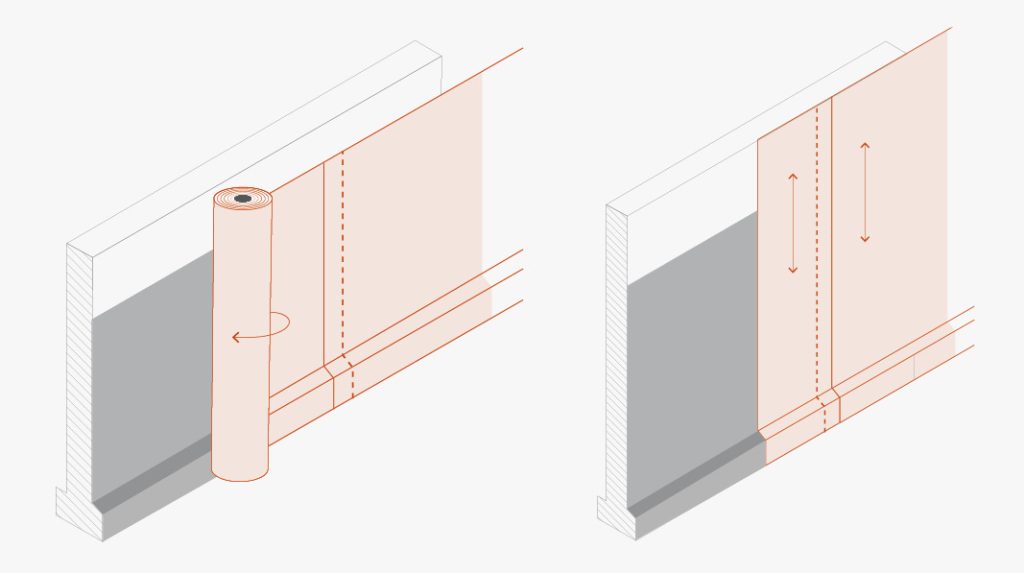
A few tips for laying TMD 1011 on vertical surfaces
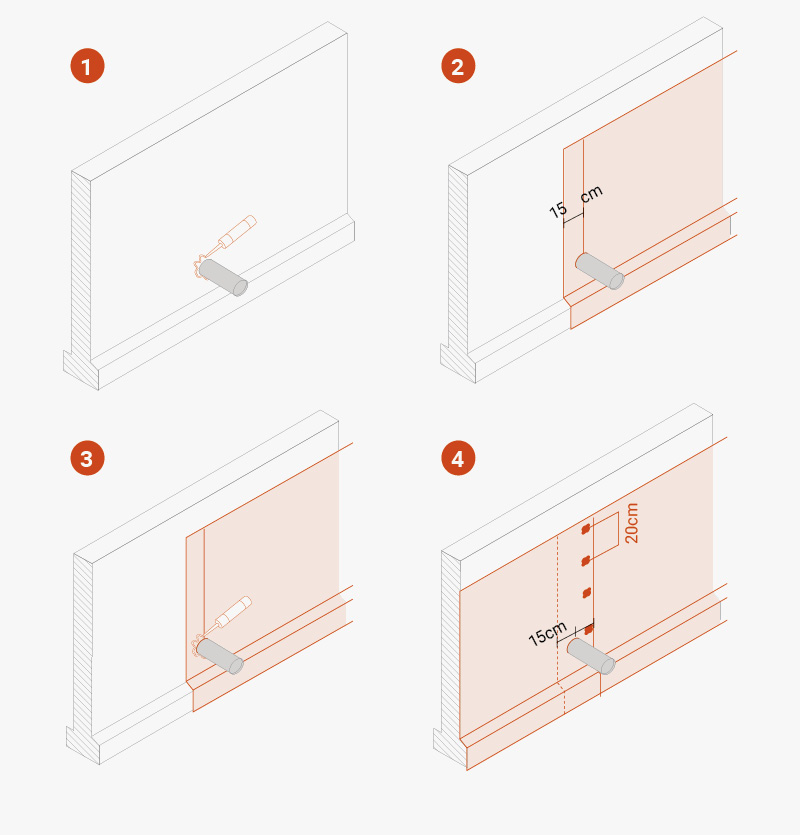
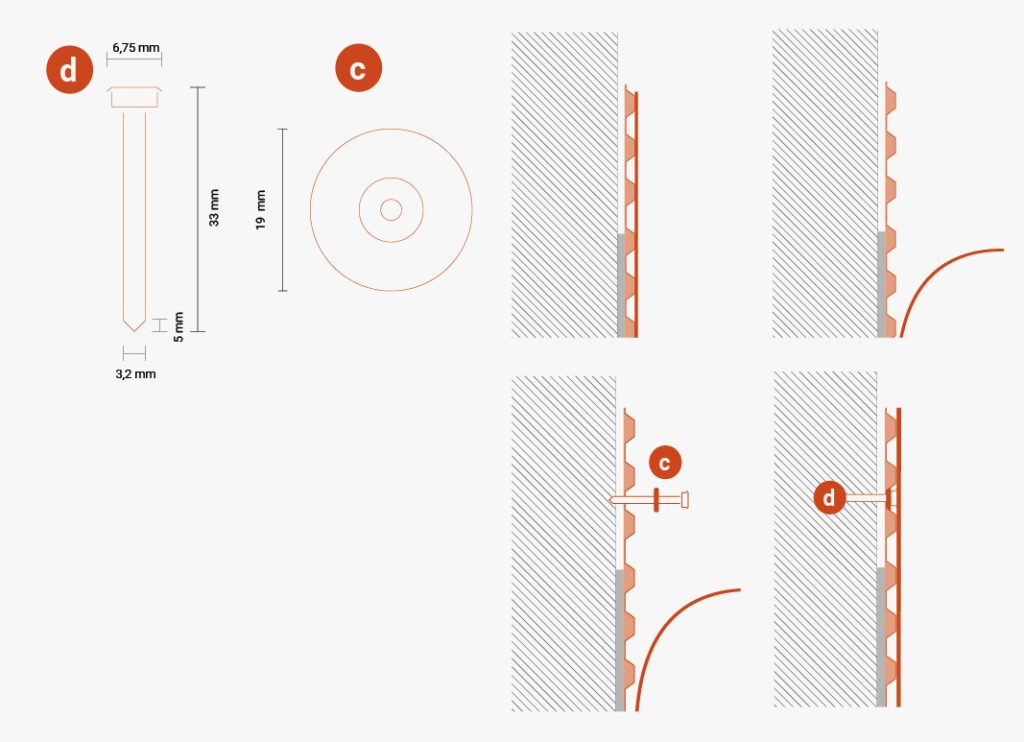
Unroll the membrane and install it vertically or horizontally: in the latter case, the width of the roll corresponds to the height of the wall to be protected. Two consecutive membranes should overlap by about 20 cm, and the studs should interlock.

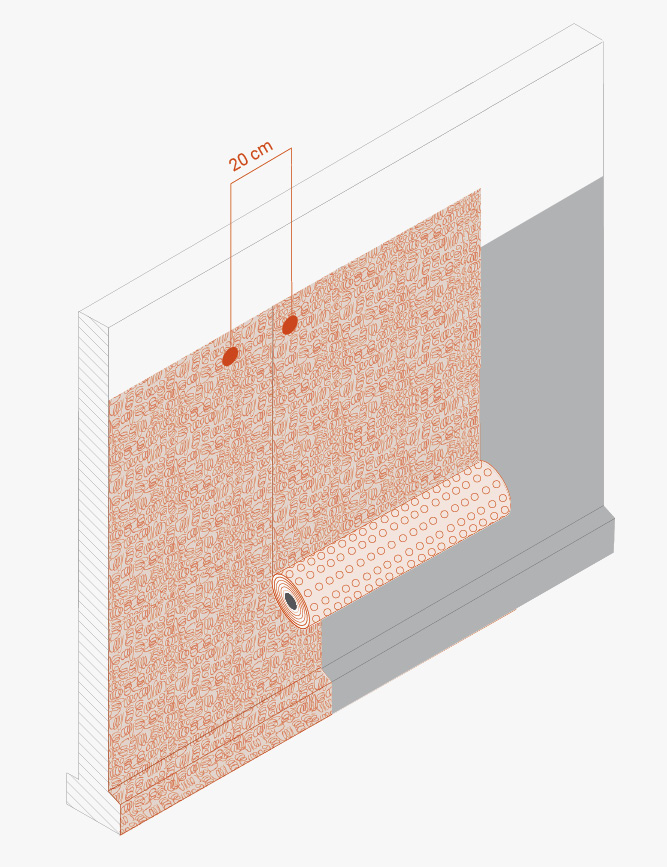
For horizontal joints, if the TMD 1011 membrane is not wide enough to completely cover the height of the installation, the first layer should be installed from the base upwards and then, keeping an overlap of at least 15 cm, the second layer should be installed by overlapping the first layer outwards (i.e. towards the side away from the wall). Install washers every 20 cm in the overlapping area.
Inlets for utility connections, such as water, gas, sewers or similar pipelines
- Place mastic sealant around the pipeline or inlet.
- Cut the TMD 1011 membrane vertically so that it extends 15 cm beyond the pipeline or inlet, trimming the membrane so that it adheres as tightly as possible.
- Put mastic sealant on the membrane so that there is a layer of mastic both above and below the membrane around the pipeline or inlet.
- Start the next installation of the membrane 15 cm before the pipeline or inlet so that the overlap around the pipeline or inlet is 30 cm. Trim again around the pipeline or inlet for watertightness.
- Install fasteners every 20 cm along the edge of the overlapping membrane.
Change of level or areas where the smooth part has been trimmed
Use T-Profile + T-Nails to seal the edge, using a sealant for the area to ensure that the edge is properly sealed.
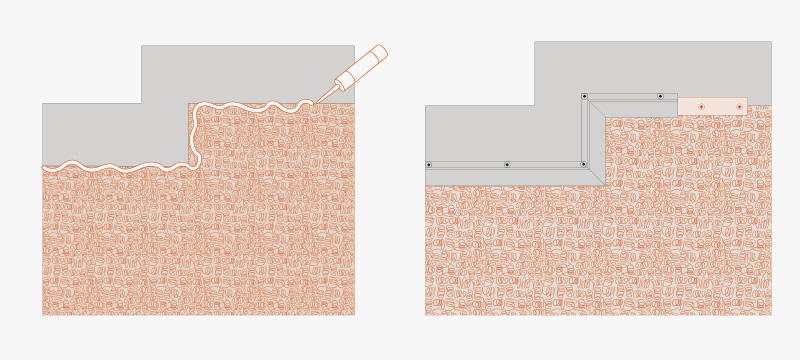
TMD 1011 should also be protected with T-Profile to prevent soil from penetrating into the gap between the wall and membrane. Then, fasten it using washers and nails with T-Nails spaced at intervals of 20-30 cm, either along the upper edge of the studded membrane or along the profile.
Drainage for diaphragms and berlin walls: a practical and safe solution
Some of the most widely used works in the civil engineering field are diaphragms and berlin walls, which counteract strong thrusts of the soil and prevent landslides and structural subsidence.
Diaphragms are supporting walls consisting of pointed vertical elements (piles) or continuous elements (walls) made of steel or reinforced concrete. They are driven into the ground to a considerable depth, whereas Berlin walls are flexible retaining structures constructed with vertical micro-piles.
Both solutions are used where it’s impossible to construct excavation walls of an adequate gradient due to the presence of other nearby structures and to the morphology of the area , which imposes limited work spaces (that would make manoeuvring large machinery impossible).
Berlin walls made of micro-piles are one of the most popular applications on construction sites for implementing waterproof retaining works. The technique allows work to be carried out on almost all types of terrain, especially when it’s necessary to use on-site systems that are smaller than in the past.
Since works are in contact with the ground, the drainage aspect should not be underestimated. If rainwater and groundwater exert pressure on the vertical wall, they may damage the waterproofing. TeMa Building Solutions therefore has the right product for this application: T-Mix Drain WP, the geocomposite that not only drains but also provides the functions of filtration, separation and stay-in-place formwork.
TeMa has acquired considerable experience with geocomposites. For many years, the company has been providing this system to replace the conventional gravel drainage system. The results are long-lasting and it’s the ideal solution: compared to conventional gravel, it’s less bulky, easily transported and quick to install. This reduces the costs of transport and implementation and on-site construction time while, last but not least, resulting in considerable savings in terms of CO2.
Fields of application
As mentioned above, diaphragms and berlin walls are widely used where space is limited. More specifically, they can be used in the construction industry, for example for underground garages in homes or commercial premises, for basements. They can also be used in river works, such as quays and piers for boats, or in earth dams and wells.
Having the experience of TeMa technicians and tested effective products such as T-Mix Drain WP at your disposal is therefore a guarantee for your construction site.
Reinforced earth structures and drainage
For the extension works at the Serravalle Retail Park shopping centre in the Piedmont region, we helped the company choose the solutions to implement and assisted with verifications.
The area covering about 2,000 sqm required some intervention work regarding reinforced earth structures and drainage. In particular, we undertook the preliminary work for extension works dating back to 2016.
To the south-west of the building, the soil was secured and then surfaces were replanted with greenery.
Let’s see how this was done in more detail.
Type of intervention
In order to make the slope in front of the complex secure, the intervention work involved constructing reinforced earth structures in several banks, more specifically 3 modules of 6 m in height each.
In addition, to manage the water coming from the hydro-geographic basin situated upstream of the area, specific surface drainage works were carried out.
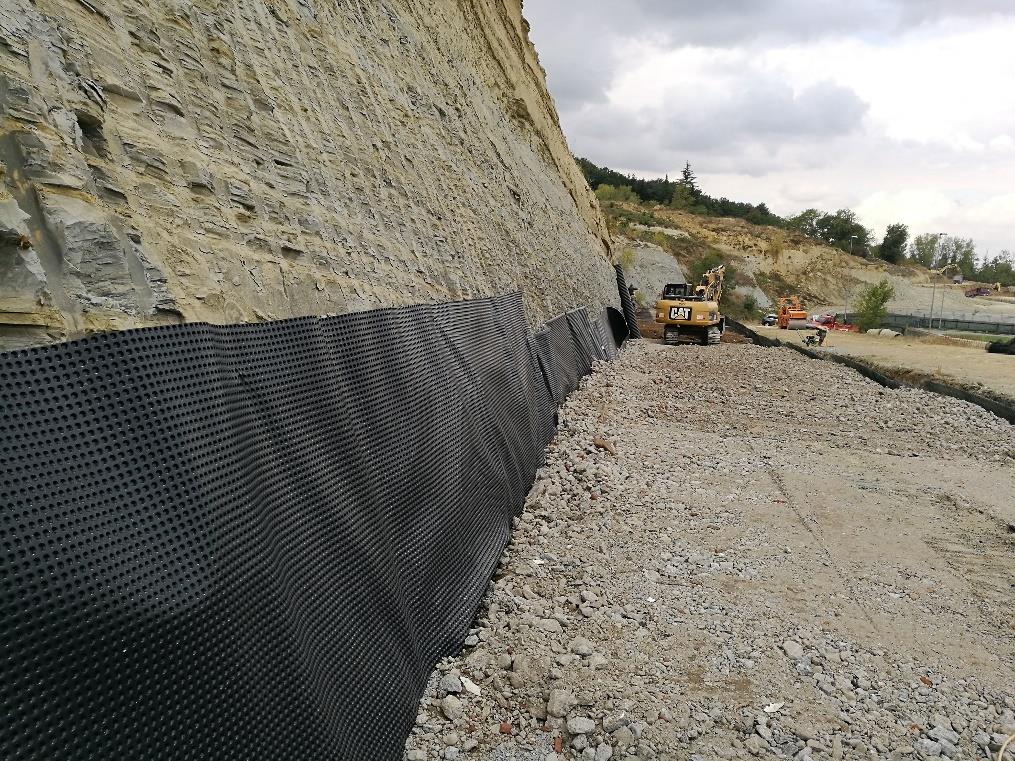
The solution from TeMa Geo Solutions
For the reinforced earth structure, 3 modules were constructed with anchorage lengths of 7 m and a strength of 110 kN/m provided by X-Grid PET PC 110 geogrids.
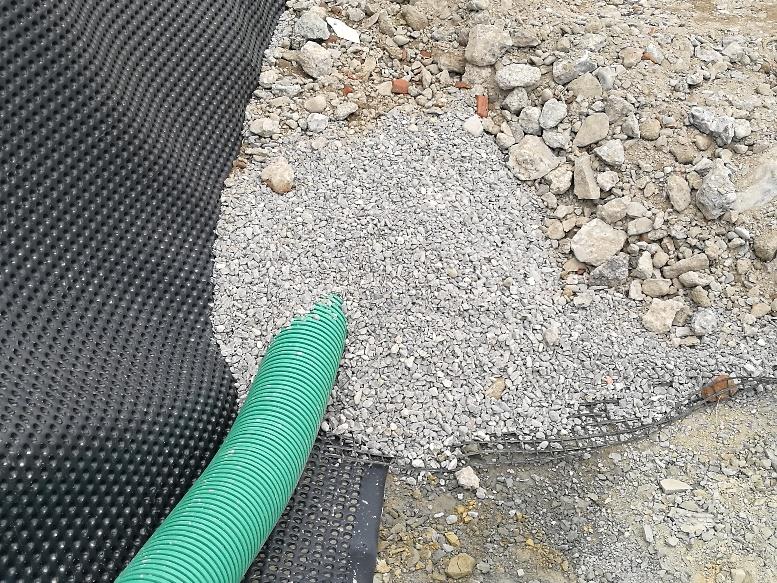
As for drainage, instead, a Membrana Nera Geo was used, the 8 mm HDPE studded membrane bonded to a filter nonwoven geotextile with a PE slotted tube at the base.
The drainage system was also installed at the horizontal contact points of each berm to prevent future water seepage into the reinforced earth structure.


Controlled landfills and the importance of isolating them
Landfills for inert, non-hazardous and hazardous waste are governed by specific laws in each country, which set out precise regulations on the construction and maintenance of these sites.
As they are virtually in the ground and designed for certain types of waste, they must meet environmental and safety standards.
Let’s take a look at everything in detail.
The risks of not isolating them
Assuming that proper disposal is essential, many types of waste can take years, even decades, to disintegrate and complete natural decomposition processes. At this stage, they produce a large amount of slurry, such as leachate, which is extremely contaminating for the soil and for groundwater.
Moreover, biogases are also produced, mainly methane and carbon dioxide, due to the breakdown of organic material, which must be controlled and could be used to produce renewable energy.
How to isolate them
Controlled landfills need to be isolated from the ground that hosts them, but to be safe they need to fulfil different functions.
Surface erosion control
Vegetation naturally protects the ground from erosion by weather conditions such as wind and rain, which would cause subsidence. While waiting for grassing to protect the sides and surface of the landfill, anti-erosion geomats, in a biodegradable and synthetic version, can be chosen according to needs.
TeMa Geo Solutions offers a wide range to choose from, which can be browsed here.
Reinforcement
A landfill site is sometimes designed and built on more or less steep slopes. If a slope is steep and the ground is unable to support itself, retaining grids need to be installed in order to prevent slippage, which would expose and damage lower layers. View all our solutions.
Drainage
Specific products, drainage geocomposites, can be used for the drainage of rainwater and leachate, which inevitably builds up and must be kept away from the ground.
Barrier
Bentonite-based products, such as Barrier Bento, allow the area to be waterproofed, including walls with high slopes and the bottom.
Capping
Landfills also have a final cover that must meet precise criteria. These include isolating waste from the ground and surface erosion control. However, minimising water seepage and blending into the landscape are equally important.
- 1
- 2