
Slopes and embankments can be used as road or railway embankments, raised flood banks and floodplains, and even vineyards, especially in a territory such as Italy, one of the countries with the largest number of UNESCO World Heritage landscapes in the world.Many of those greened terraces are true reinforced earth structures, with their stability guaranteed by a well-tested construction technique.
Stability for slopes and embankments
Reinforced earth structures are retaining works that allow slopes and embankments to be supported, including steep slopes. They do not involve the use of concrete constructions, which would be more detrimental to the landscape.
The soil has a natural capacity for compressive strength. When combined with geosynthetic grids (which have excellent tensile strength), they create a stable system, as the features of the two components provide a high-performance composite.
The open mesh structure allows reinforcement geogrids to develop passive resistance along the transverse ribs, as well as creep resistance of the geosynthetic grid in relation to the soil. The TeMa Geo Solutions range includes X-Grid geogrids, available in a variety of models depending on the type of project.
How to position the geogrid in the layering of a terrain?
Each slope needs to be carefully and expertly engineered. However, in addition to the need to reinforce the raised earth structure with geogrids, it is essential to ensure surface erosion control using synthetic or natural erosion control mats and shaping with electro-welded wire mesh formwork.
The X-Grid geogrid must be applied to each ‘block’ of soil supported by the formwork, positioned between the backfill soil and the erosion control mat. An external wrap-around part, measuring no more than 150 cm, must be provided for the formwork system by installing formwork stiffening ribs approximately 30 cm apart.
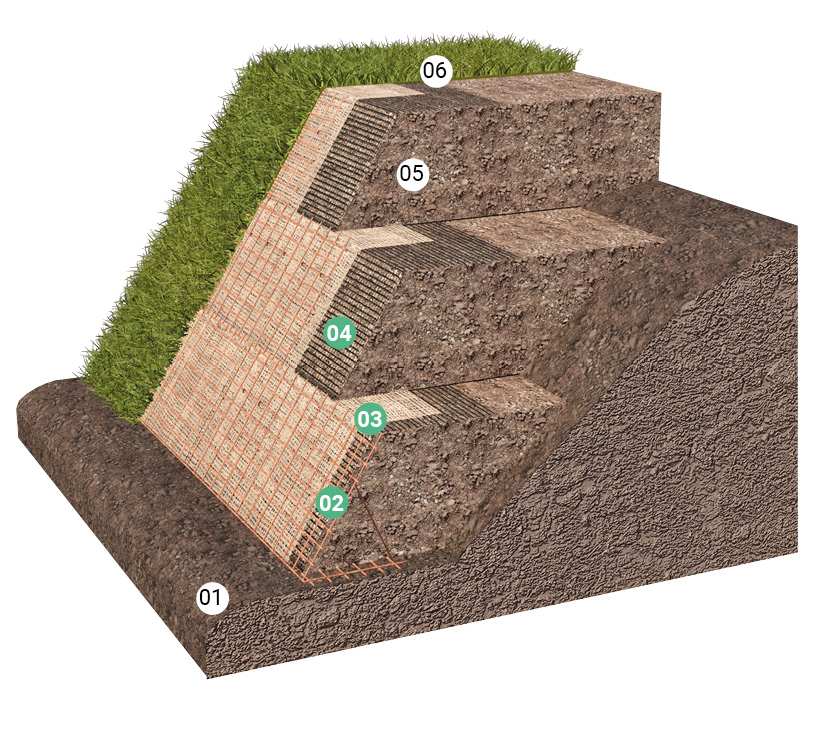
- Foundation soil
- Metal formwork
- Erosion control mat
- Geogrid
- Backfill soil
- Grassed surface




