Soil erosion is an almost inevitable natural phenomenon that has become a greater concern in recent years due to the worsening climate situation – in Italy, for example, 132 extreme weather events were recorded between January and July 2022, a higher number than the annual average over the last decade – combined with long periods of drought.
Strong winds, heavy rain, hail and runoff tend to remove the surface layer of exposed soils, which often include organic matter and seeds. Climate change facilitates erosion, making it not only inevitable but also hazardous if left uncontrolled.
It’s essential to counter or mitigate the phenomenon: soil provides us with food, biomass and raw materials; human activities take place on it and it’s part of the landscape and our cultural heritage.
Which structures are more subject to surface erosion?
The areas of application most affected by the erosive action of the climate are:
- slopes and the sides of landfills and contaminated sites, and those that have been grassed for appreciable aesthetic improvement;
- reinforced earth structures, more specifically terracing in vineyards and the embankments of canals or rivers;
- ascending/descending ramps from flyovers, tunnel entrances and noise barriers on roads and railways;
- dry, rocky slopes, of all angles, that shape the terrain of Italy.
The effects of surface erosion
The uncontrolled removal of the surface topsoil and the failure of vegetation to take root results in ‘thinning’ of the soil and a risk to the stability of sloping areas.
What can be done to prevent surface erosion?
We should begin by pointing out that a case-by-case assessment is required that considers many variables, such as the nature and uniformity of the soil, the slope gradient, the type of slope (dry or rocky) and the weather conditions in the area where intervention work is to be carried out.
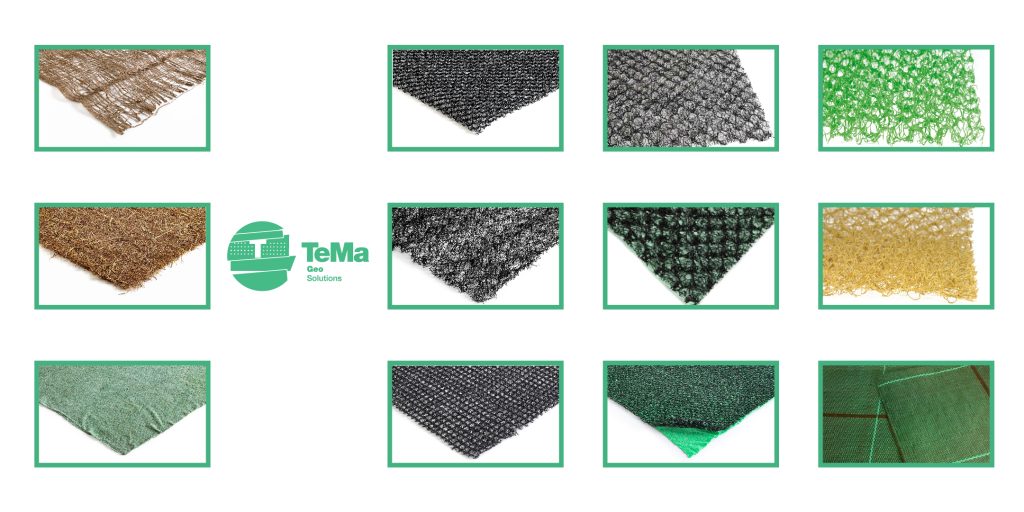
In general, vegetation, whatever type it is, has a natural ability to protect soils from erosion. So the best course of action is to quickly encourage grassing and then apply biodegradable mats made of jute, straw, coconut and cellulose fibre, which can also be pre-seeded.
TeMa Geo Solutions recommends biomats such as Ecovermat, Ecovermat P and PC, and Ecovernet.
Alternatively, or combined with these, synthetic geomats, mainly made of polymer monofilaments, can be used.
Once laid, they are covered with another layer of soil: in this way, the roots of growing vegetation will become entangled with the geomat, creating an almost permanent erosion protection system.
Once again, TeMa Geo Solutions offers a wide range of geomats to choose from.

Uncertain about what to choose? We can help you. CONTACT US!