TeMa Geo Solutions: geotechnical solutions
The TeMa Geo Solutions division has developed considerable experience in geotechnical applications and developed technologies and products, thereby ensuring that designers can meet increasingly strict regulations concerning the environment and the landscape.
These applications are for the protection, maintenance, retention, reinforcement and drainage in the field of major environmental projects, involving products that provide innovative efficient and long-lasting solutions.
We are aware that a kind of public resistance to sustainability announcements has already begun. We are therefore interested in helping companies that are taking appropriate action to protect the environment. This is not only to ensure that they can better comply with regulations but also, and above all, to increase the effectiveness and credibility of their work.
TeMa Geo solutions in applications
The areas of expertise of TeMa Geo Solutions include:
- football fields
- landfills and contaminated sites
- tunnels
- reinforced soil retaining structures
- dry slopes
- grassy road and railway embankments
- roads
- drainage ditches
- horse training and racing tracks.
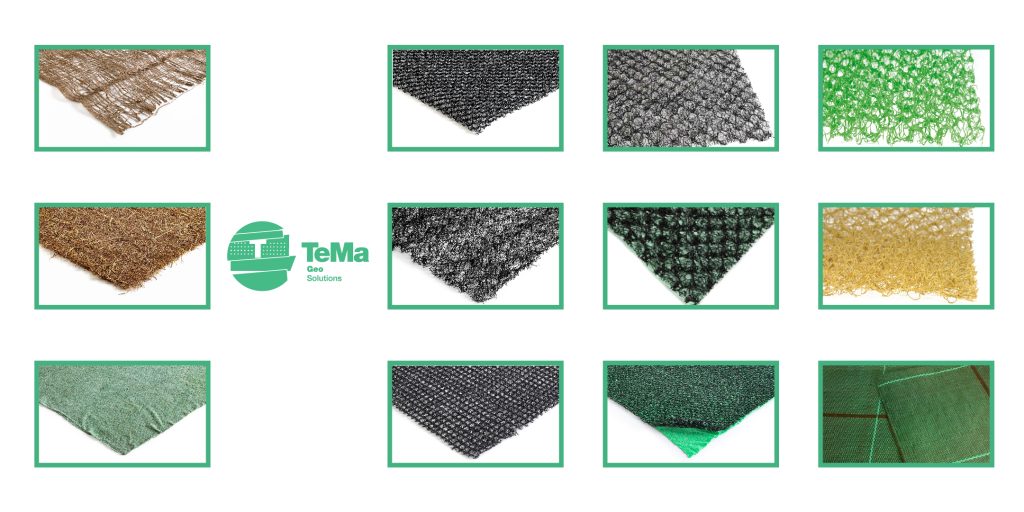
Products and functions: a range starting with geosynthetics
Geogrids are structural elements used to reinforce soils in the construction of retaining walls, block retaining walls, reinforced soil retaining structures, landfills and contaminated sites. The open mesh structure allows the reinforcement geogrids to develop ‘passive’ resistance at the transverse ribs, thus effectively increasing their inherent stabilising effect and enabling the system to withstand significant levels of stress.
The TeMa Geo Solutions range includes uniaxial or biaxial X-Grid geogrids made of fibreglass, polyester or PET coated with a polymer layer, coupled, or not, with a nonwoven geotextile, to be chosen to suit the project.
Offering products such as bentonite geocomposites, drainage geocomposites, facings, erosion control mats and essential accessories, the TeMa Geo Solutions range fulfils various functions for the retention anddrainage of rainwater and groundwater.
The TeMa Geo world offers its long-standing (since 1993) expertise and experience in the polymer-based product category (geosynthetics). Over the years, research at its in-house labs has enabled the development of solutions that integrate with the environment in a more specific sense, such as biodegradable erosion control mats, and in a broader sense, such as geomats and studded membranes.
TeMa also offers cutting-edge geotechnical solutions for vineyards
This is not surprising, as the TeMa Geo headquarters are situated on the eastern edge of the Prosecco hills, a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The company therefore has made its experience available to preserve and protect the viticultural landscape with its products for erosion control, reinforcement and ground drainage in an environment subject to the passage of agricultural vehicles. Click here to download the specific catalogue.
- Published in Drainage geocomposites and membranes, Erosion mats, GEO, Geogrids, Landfills, Reinforced earth structures, Roads, Synthetic turf soccer fields - Accessories, Tunnels
Cycle and pedestrian paths: solutions to make them safer and more attractive.
Longer days, milder afternoons, a great desire to spend time outdoors and perhaps get some physical exercise, but also go to work and school or visit a friend… These are all good reasons for using, when available, cycle and pedestrian paths, possibly far from urban traffic.
The advantages of sustainable mobility
We are increasingly talking about environmental sustainability and the physical and psychological benefits of physical exercise:
- Less air and noise pollution caused by traffic.
- Reduced transport costs.
- Greater freedom of movement.
- Enhanced green areas in cities.
- Better quality of life by doing a bit of sport on a daily basis.
TeMa Geo Solutions for safety and urban benefits
‘Unequipped’ roads can be hazardous for those who choose to get around by bicycle: for this and environmental reasons, cycle and pedestrian paths are the ideal solution, as they are increasingly becoming part of local government mobility plans.
TeMa Geo Solutions offers all its experience by combining reinforced earth structures and their feature of being green, with cycle and pedestrian paths.
An embankment can be made or a road widened with its sides sloping at 65°/70° using the T-System (consisting of formworks, X-Grid PET geogrids and K-Mat FG Green erosion control mats as facing), thereby making the path safe and allowing a slope to turn green again. Making a slope green again provides a natural erosion control function: to encourage it, TeMa Geo Solutions recommends installing natural or synthetic mats. To make the structure stable, the T-System for reinforced soils adopted by TeMa involves using X-Grid PET geogrids.
Controlling surface erosion with biomats and geomats
Soil erosion is an almost inevitable natural phenomenon that has become a greater concern in recent years due to the worsening climate situation – in Italy, for example, 132 extreme weather events were recorded between January and July 2022, a higher number than the annual average over the last decade – combined with long periods of drought.
Strong winds, heavy rain, hail and runoff tend to remove the surface layer of exposed soils, which often include organic matter and seeds. Climate change facilitates erosion, making it not only inevitable but also hazardous if left uncontrolled.
It’s essential to counter or mitigate the phenomenon: soil provides us with food, biomass and raw materials; human activities take place on it and it’s part of the landscape and our cultural heritage.
Which structures are more subject to surface erosion?
The areas of application most affected by the erosive action of the climate are:
- slopes and the sides of landfills and contaminated sites, and those that have been grassed for appreciable aesthetic improvement;
- reinforced earth structures, more specifically terracing in vineyards and the embankments of canals or rivers;
- ascending/descending ramps from flyovers, tunnel entrances and noise barriers on roads and railways;
- dry, rocky slopes, of all angles, that shape the terrain of Italy.
The effects of surface erosion
The uncontrolled removal of the surface topsoil and the failure of vegetation to take root results in ‘thinning’ of the soil and a risk to the stability of sloping areas.
What can be done to prevent surface erosion?
We should begin by pointing out that a case-by-case assessment is required that considers many variables, such as the nature and uniformity of the soil, the slope gradient, the type of slope (dry or rocky) and the weather conditions in the area where intervention work is to be carried out.
In general, vegetation, whatever type it is, has a natural ability to protect soils from erosion. So the best course of action is to quickly encourage grassing and then apply biodegradable mats made of jute, straw, coconut and cellulose fibre, which can also be pre-seeded.
TeMa Geo Solutions recommends biomats such as Ecovermat, Ecovermat P and PC, and Ecovernet.
Alternatively, or combined with these, synthetic geomats, mainly made of polymer monofilaments, can be used.
Once laid, they are covered with another layer of soil: in this way, the roots of growing vegetation will become entangled with the geomat, creating an almost permanent erosion protection system.
Once again, TeMa Geo Solutions offers a wide range of geomats to choose from.

Uncertain about what to choose? We can help you. CONTACT US!
New solutions in road construction and/or repairs
The safety of road infrastructures is the main goal, and maintenance work – whether preventive or supplementary – is systematic.
Road surfaces withstand heavy traffic loads and atmospheric changes with significant variations in temperature. Constant maintenance is therefore required in order to ensure even surfaces and the stability of structural elements.
Let’s look at the main factors involved in building new roads or maintaining roads.
Controlling surface erosion
Erosion is largely due to freeze/thaw cycles, which make asphalt less elastic and therefore more prone to internal voids. Such voids allow water to penetrate into underlying layers, gradually eroding the structure.
In addition, heavy traffic loads, especially heavy vehicles, cause deformation of the surface layers: this results in water penetration, which “softens” the structure and makes it less resistant.
Anti-capillary drainage
The water capillarity, i.e. the ability of liquids to move in micro-spaces even against the force of gravity, is a rather complex concept closely monitored in the construction industry. With the help of pressures exerted on lower layers, water rises upwards, dragging the finer components of materials with it and causing deformation.
It is therefore necessary to provide a drainage geocomposite, a three-dimensional membrane obtained by bonding two or more synthetic components in order to convey fluids to the exterior and prevent them from rising.
You can discover all our solutions here.
Reinforcement
It may sometimes be necessary to install reinforcement grids, especially if there is a more or less pronounced slope that would cause a road shoulder to slide downwards.
The choice of the most suitable type of reinforcement, and therefore also of the position of the geogrid in the layering, clearly depends on the problems to be faced i.e. reinforcing the surface area to limit the spread of cracks to underlying layers, improving the load-bearing capacity and reducing the stresses transmitted to lower layers, or providing a separation (and anti-contamination) function.
Discover all our solutions here.
Stabilisation
During intervention works, softer soils may be encountered, which may be subject to instability or even collapse in the early stages of intervention works. Even if this should not jeopardise the feasibility of the works, there is still the risk that the minimum legal safety requirements will be compromised.
Also in this case, geosynthetic products are the solution to the problem, as they absorb tensions at least until the intervention work achieves structural stability.
Discover the solutions in the X-Grid line here.
- Published in Drainage geocomposites and membranes, Erosion mats, GEO, Geogrids, Roads
Cycle/pedestrian paths: when we get back onto our saddle, we’ll know more about them…
We know that our bike has become a mirage. But we can promise ourselves to use it more when this period of seclusion is over. Meanwhile, why don’t we take advantage of the time available to discover interesting things all around us? For example, cycle paths. Let’s start at the beginning.
What is the correct definition of a cycle/pedestrian path?
It’s where you can ride your bike, of course. But, can pedestrians walk on it too? What is the direction of movement? Then there are increasingly more complex questions, such as: has it been built as a separate cycle path or as a reserved lane? Is it a cycle/pedestrian path or a vehicular/cycle path? In short, there are many features that a cycle/pedestrian path must have in order to be defined as such. Let’s take a look at them together.
The cycle/pedestrian path was invented to allow pedestrians and bikes to get about. Such paths require cyclists to respect pedestrians and get off their bike whenever necessary to avoid getting in the way. Consequently, they are not paths for the exclusive use of cyclists.
Creating these kinds of paths encourages people to get about without using a car, thanks to these dedicated spaces, where they can feel safe from urban traffic.
How do you build a cycle/pedestrian path?
In 2018 TeMa Geo Solutions built a cycle/pedestrian path in Cozzuolo di Vittorio Veneto (TV). One of the main aims of the project was to improve road safety in an area that is a gateway to the city and where a city park is situated, used by families and children.
First of all, we enlarged the road and the nearby roundabout in order to create the necessary space for inserting the path. The enlargement was facilitated by the construction of a reinforced earth escarpment, for which reinforced geogrids were used. Installed in the ground, they create friction and enable the system to withstand significant levels of stress. The intervention work, designed on the basis of a single berm positioned at about 2 metres above ground level, allowed pedestrian and cycle traffic in an area that had been dangerous from the outset.
Looking on the bright side, when you get back onto your saddle, you’ll be more aware of what’s under your wheels. Enter the TeMa world, visit our website.