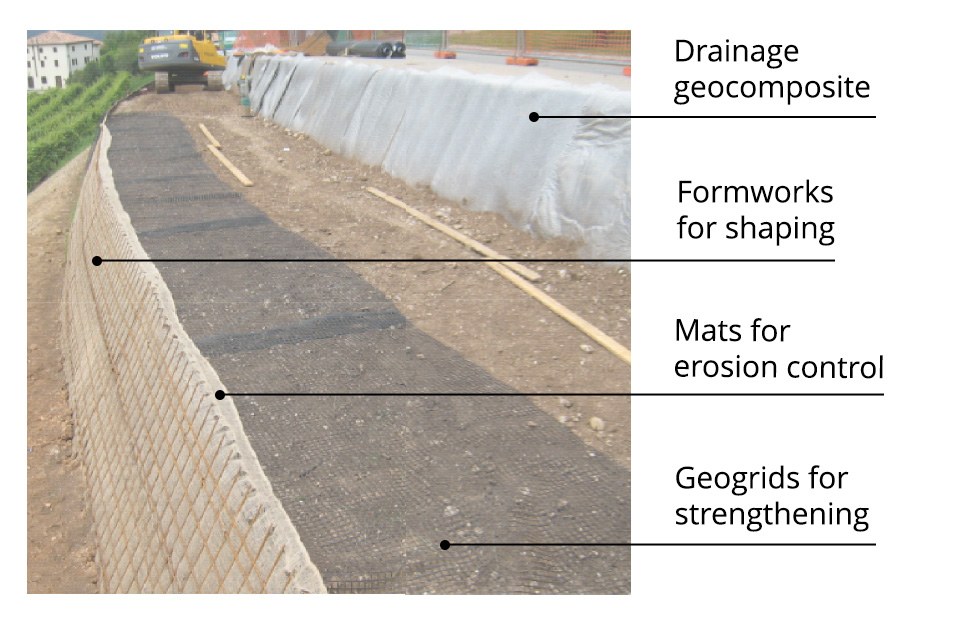
System for reinforced soil retaining structures
T-System is the system from TeMa Geo Solutions that includes various components for strengthening, surface erosion control, drainage and retaining used in the construction of reinforced soil retaining structures: innovation that we’ve been exploring here at TeMa since our inception 30 years ago, and that is now one of our hallmarks. Let’s take a more detailed look below.
Components for strengthening
Designed for strengthening, the knitted X-Grid PET C geogrids are made from high-strength polyester yarn, with a protective polymer coating. They deliver tensile strength in the 20 kN/m to 800 kN/m range.
Components for erosion control
They protect the face of the structure from erosive agents, like wind and driving rain, until the vegetation has had time to establish. TeMa Geo Solutions offers natural solutions made from cellulose fibres, like Ecovermat, or jute fibres, like Ecovernet, as well as synthetic solutions made from monofilaments (K-Mat F), polypropylene (K-Mat FA) or fibreglass (K-Mat FG Green).
Components for drainage
Drainage geocomposites like Q-Drain are used to address the problem of water seeping into the backfill.
Components for retaining
We have a line of facings made from electrically welded wire mesh — with inclinations ranging from 65° to 80° — to ensure the exposed face is straight.
Practical tips
On site
System components must be stored well away from machinery, and suitably protected from dust or residues from work on site.
To avoid excessive overlaps and waste, the X-Grid geogrids must be cut to size using a suitable metal stand with metal trestles supporting a circular rod to be inserted inside the roll.
Erosion control components — whether biodegradable or synthetic — must be stored in a dry place and not in direct contact with the natural ground, so as to avoid laying problems later on.
Metal formwork must be stored well away from areas where machinery is operating, and carried in only when it is time to install.
During assembly, it is best to apply U-shaped strips of rubber or metal so that the geogrids can be wrapped correctly over the formwork without getting caught on the top of the bars. (see photo)
Special instructions
We advise against backfilling with silty and clayey material; at the very least, only use this kind of material after mixing it with aggregate.
The full range of system components comes with instructions on the relevant procedures to be followed. Contact us, we’ll be happy to provide case studies and full information.
- Published in Erosion mats, GEO, Geogrids, news, Reinforced earth structures, Reinforced earth structures - Drainage, Reinforced earth structures - Erosion control
TeMa at the 12th International Conference on Geosynthetics.
We too will be at the 12th edition of the International Conference on Geosynthetics that will take place in Rome, at the Parco della Musica auditorium from 17 to 21 September 2023, and which will involve a full programme of meetings between professionals (further information about the events here).
Four days of training and information meetings on geosynthetics, exploring all sub-types: woven and non-woven geotextiles, geogrids, geonets, geomats, drainage and reinforcement geocomposites, and geomembranes.
Geosynthetics are becoming increasingly popular in applications and fulfil various functions (often combined). For example:
- Drainage – drainage geocomposites and geonets.
- Filtration and Separation – woven geotextiles and non-woven geotextiles.
- Reinforcement – woven geotextiles and geogrids.
- Protection of waterproofing – studded membranes with truncated conical or star-shaped studs.
- Erosion control – geonets, geomats, biotextiles.
- Mechanical protection – non-woven geotextiles, composite geotextiles.
- Special applications – various geosynthetics made to specific requirements.
The main topics discussed will cover various fields of application, including anti-seismic design to road and railway embankments, erosion control, filtration and drainage functions, as well as an analysis of case studies.
The world of research is continuously evolving and the scheduled meetings will provide an excellent opportunity for sharing experiences and recent technical developments with engineers, geologists, consultants, contractors and whoever is involved in research and using geosynthetics.
During the exhibition event visitors will be able to take part in technical conferences, the Giroud lecture, special lectures and short courses , as well as visit the exhibition hall to meet manufacturers.
TeMa has thirty years of experience in using geosynthetics
The international event, entitled ‘Leading the way to a resilient planet’, fully represents the reason why TeMa began to manufacture and experiment with geosynthetics from the mid-1990s onwards: to research the most suitable technologies and materials for use in the construction of buildings and geotechnical works.
We have been involved in continuous interaction, also due to an increased awareness of major environmental issues. This has enabled us to broaden our range of products and expand in 80 countries worldwide.
Today, our catalogue includes many products that meet specific requirements for landfills, tunnels, road embankments, river banks and reinforced earth structures, gradually increasing performance for surface erosion control, rainwater drainage, and the reinforcement of grassy slopes.
The geosynthetics sector is rapidly developing and we are making huge investments, especially in research, so as to supply our customers with the best solutions, also tailor-made, for their projects. We share the same ‘urgency’ as our partners to pursue our unwavering ideal of respecting the environment and the hydrogeological protection of the land.
We look forward to seeing you in Rome from 17 to 21 September 2023, at Stand 22.
Meanwhile, you can discover all the details about the event here.
Technical considerations in building reinforced soil walls
Reinforced soil walls have proved highly popular in recent years and are produced wherever possible, taking the place of concrete-faced soil retaining wall systems.
Employed in a range of different environments, they bring significant advantages, both financial and environmental. Indeed, unlike concrete-faced soil retaining wall systems, they:
- are sustainable because they give a vegetated finish;
- are a great space-saving solution, with slopes as steep as 80° (compared to the 30-40° of natural soil embankments);
- result in less pollution given the smaller number of trucks required to carry construction materials;
- make use of the excavated earth for backfilling, provided it is compatible with stability standards, meaning no more material needs to be brought in;
- blend seamlessly with their surroundings once the slopes are grassed over, without becoming a blot on the landscape of our villages.
Whatever the case, before planning the work, there are a number of aspects and data to be taken into consideration.
Preliminary data needed
To start with, all essential technical information must be procured in order to be able to assess the feasibility of the project, such as:
- geological testing of the area on which the wall is planned to be built
- topographical surveys
- meaningful cross-sectional drawings showing the current condition
- geometry of the planned wall (face angle, height, division into tiers, slope on top)
- external loads applied to the structure (top loads in the event it needs to accommodate a car park or a road)
- what earthquake risk zone the area is in
- geotechnical properties (angle of shearing resistance, cohesion and density) of the earth behind the future wall, of the foundation soil, and of the backfill
- whether there are perched aquifers or seepage of a different nature.
At this point, the next step is to check design calculations using specific software.
Checking design calculations
Checking is performed to assess both internal and external stability. The following tests are carried out in the former case:
- reinforcement strength test, which assesses possible failure mechanisms and determines the spacing, length and tensile strength of the geosynthetics due to be laid
- pull-out test to check that the reinforcement applied does not break or slide out
- direct sliding test, to ensure there is no translational movement across the installation planes
- wrap-around test, to ensure that the length wrapped around the top of each individual layer is stable.
The checks to be carried out during the project’s execution to assess external stability consist in sliding, overturning, bearing capacity and global failure analysis.
Do you want to chat with one of our experts to find the solution that best suits your requirements?
We have 30 years of experience in the industry and can give you access to materials and solutions offering specific performance. Contact us!
Do you want to learn more about the full TeMa Geo Solutions product range for reinforced earth structures? Click here.
Reinforced earth structures and drainage
For the extension works at the Serravalle Retail Park shopping centre in the Piedmont region, we helped the company choose the solutions to implement and assisted with verifications.
The area covering about 2,000 sqm required some intervention work regarding reinforced earth structures and drainage. In particular, we undertook the preliminary work for extension works dating back to 2016.
To the south-west of the building, the soil was secured and then surfaces were replanted with greenery.
Let’s see how this was done in more detail.
Type of intervention
In order to make the slope in front of the complex secure, the intervention work involved constructing reinforced earth structures in several banks, more specifically 3 modules of 6 m in height each.
In addition, to manage the water coming from the hydro-geographic basin situated upstream of the area, specific surface drainage works were carried out.
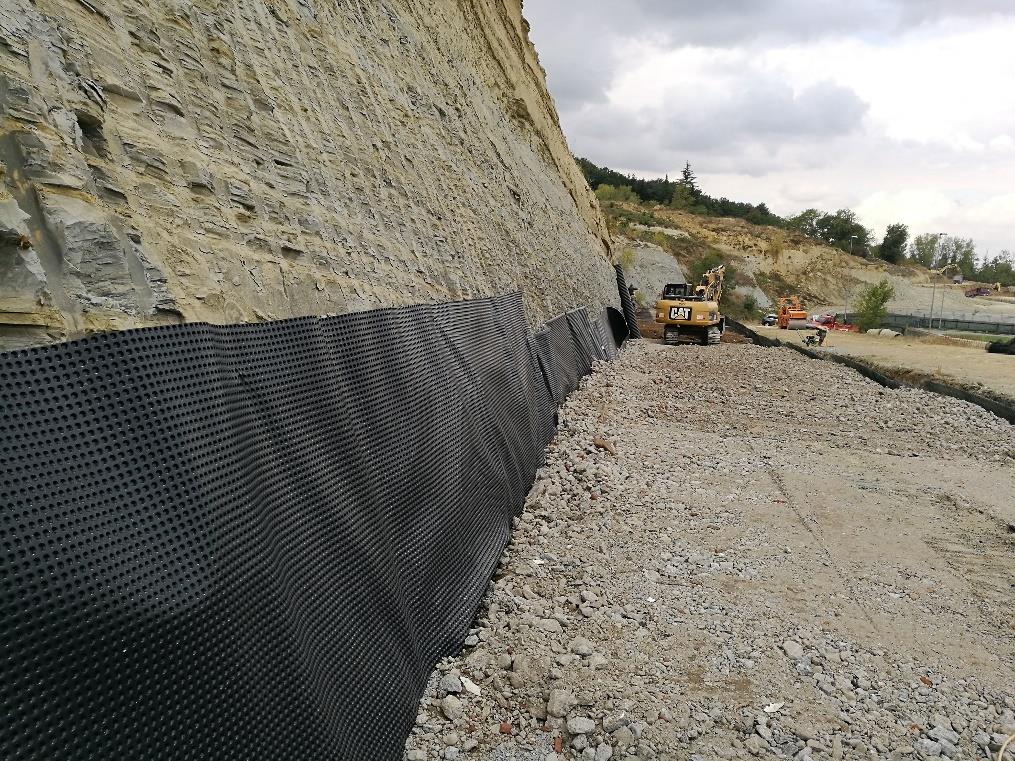
The solution from TeMa Geo Solutions
For the reinforced earth structure, 3 modules were constructed with anchorage lengths of 7 m and a strength of 110 kN/m provided by X-Grid PET PC 110 geogrids.
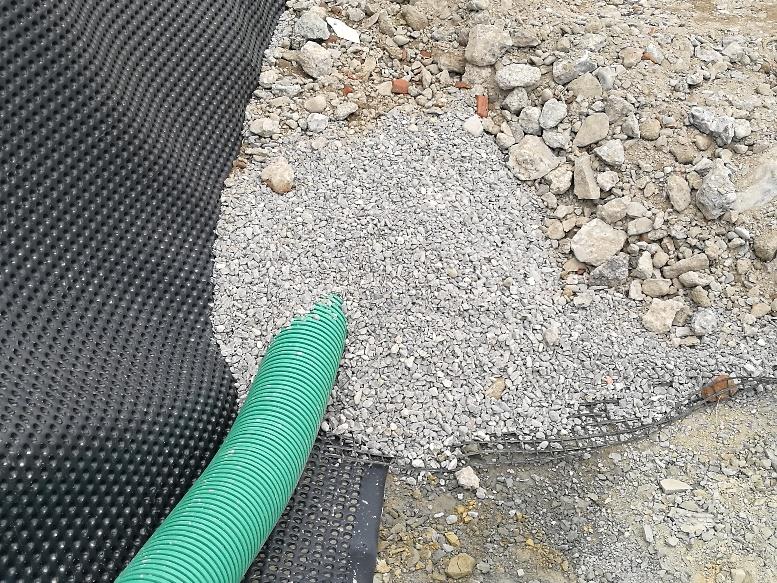
As for drainage, instead, a Membrana Nera Geo was used, the 8 mm HDPE studded membrane bonded to a filter nonwoven geotextile with a PE slotted tube at the base.
The drainage system was also installed at the horizontal contact points of each berm to prevent future water seepage into the reinforced earth structure.


Geosynthetics: Advantages and Applications
Our passion for work does not stop, it simply continues at our company, in a little more limited way. You certainly cannot see us running up and down building sites or going in and out of our research labs, but we can assure you that we are still working on our production of geosynthetic products with the same commitment and perseverance in order to formulate new projects and develop ideas that we will see materialised soon, once everything has ended.
TeMa and Geosynthetic Products
TeMa Geo is the TeMa division created almost thirty years ago with the aim of exploring and expanding the world of geosynthetics, which it still does today. By “geosynthetic products” we generally mean all categories of synthetic coverings that are not only used in contact with earth or other building materials but are also appreciated for their use in various building fields. In the building industry, their main advantage is that they are user-friendly in technical terms, which is why engineers and planners prefer them to other technical solutions.
The Advantages of Geosynthetics
The advantages of geosynthetic options not only lies in the fact that they are easy to use but also in their cost-effectiveness: certainly less expensive, they provide excellent performance that remains unchanged over time. Furthermore, their versatile use makes them the ideal solution to various on-site problems.
Geosynthetic Products “In the Field”: the Serravalle Project
In more practical terms, today we want to tell you about the intervention works we carried out in the Piedmont region in 2016. It involved extension works for Serravalle Retail Park. In preparation for the works, we had to make the slope in front of the new complex safe. In order to proceed, we had to prepare several reinforced soil structures, separating them into banks, and solve the problems of surface drainage for the management of water, whose catchment area was located above the area.
For works of such magnitude, we used geogrids from the XGrid PET-PVC range as a structural element. In addition, to avoid any seepage in the future, drainage elements were installed close to the reinforced structures of the horizontal sections of each berm. This is just one of our products and one of the many fields of application explored by TeMa.
To discover all our membranes, visit our section dedicated to products.
- Published in GEO, Geogrids, Reinforced earth structures, Reinforced earth structures - Drainage