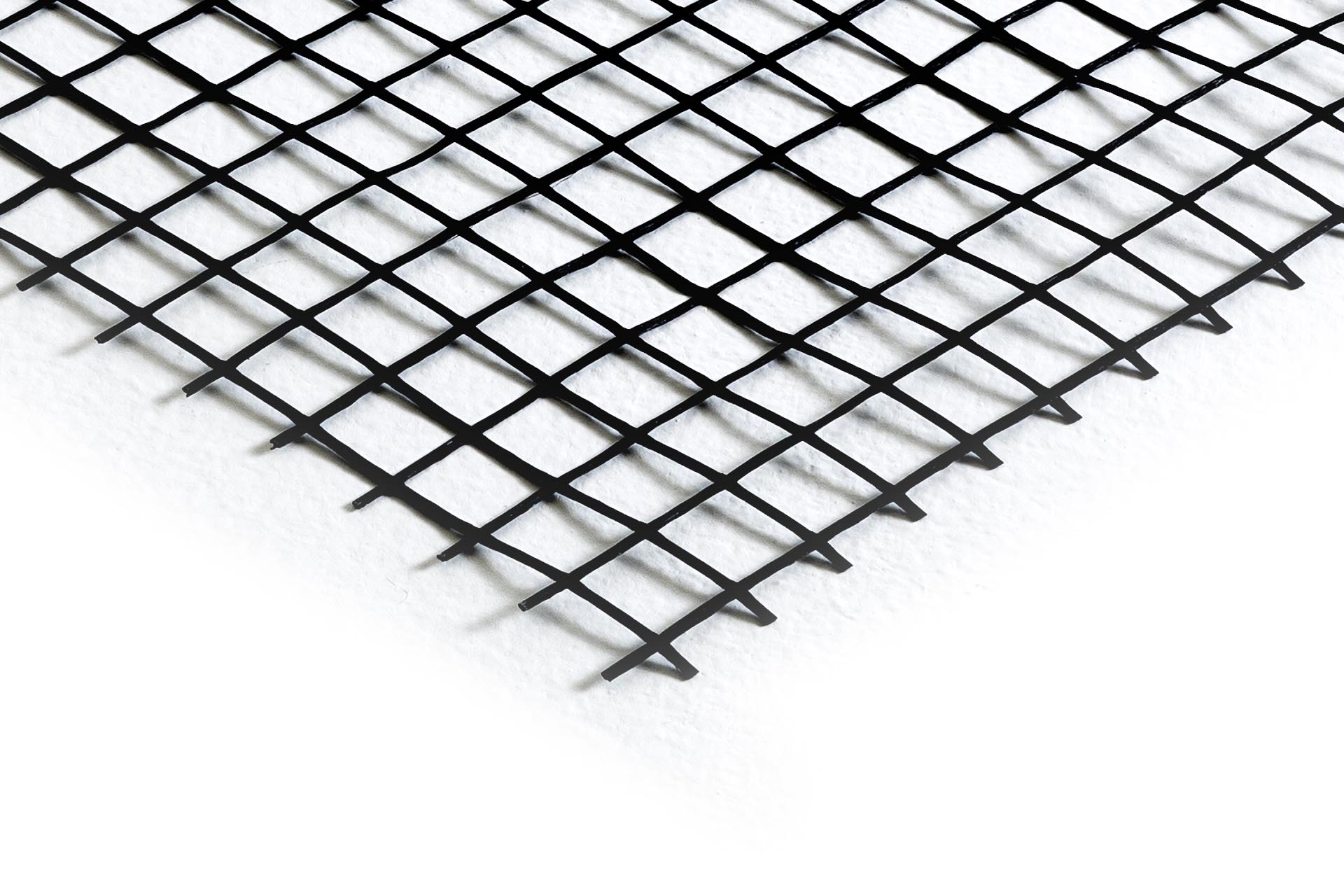
Controlled landfills and the importance of isolating them
Landfills for inert, non-hazardous and hazardous waste are governed by specific laws in each country, which set out precise regulations on the construction and maintenance of these sites.
As they are virtually in the ground and designed for certain types of waste, they must meet environmental and safety standards.
Let’s take a look at everything in detail.
The risks of not isolating them
Assuming that proper disposal is essential, many types of waste can take years, even decades, to disintegrate and complete natural decomposition processes. At this stage, they produce a large amount of slurry, such as leachate, which is extremely contaminating for the soil and for groundwater.
Moreover, biogases are also produced, mainly methane and carbon dioxide, due to the breakdown of organic material, which must be controlled and could be used to produce renewable energy.
How to isolate them
Controlled landfills need to be isolated from the ground that hosts them, but to be safe they need to fulfil different functions.
Surface erosion control
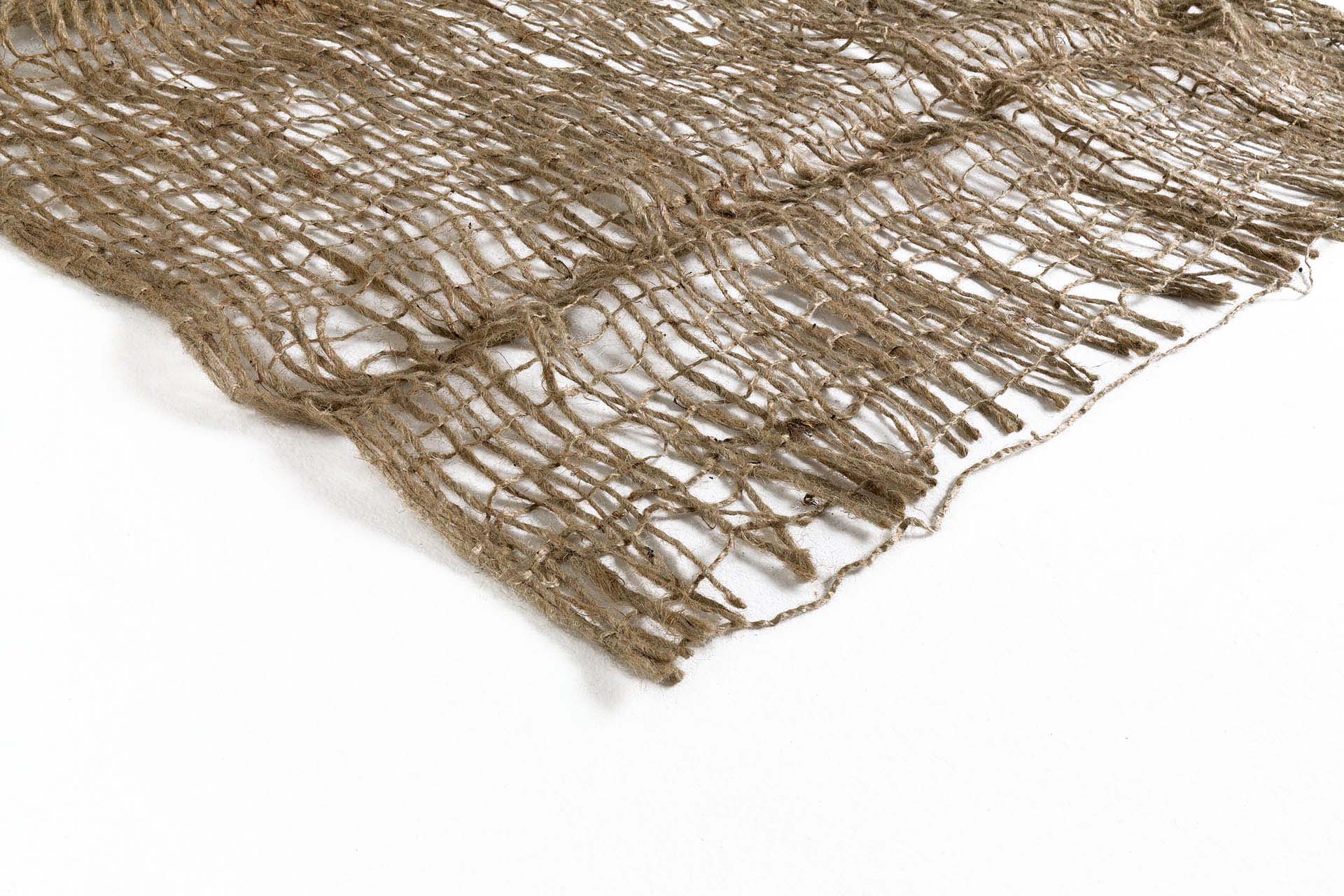
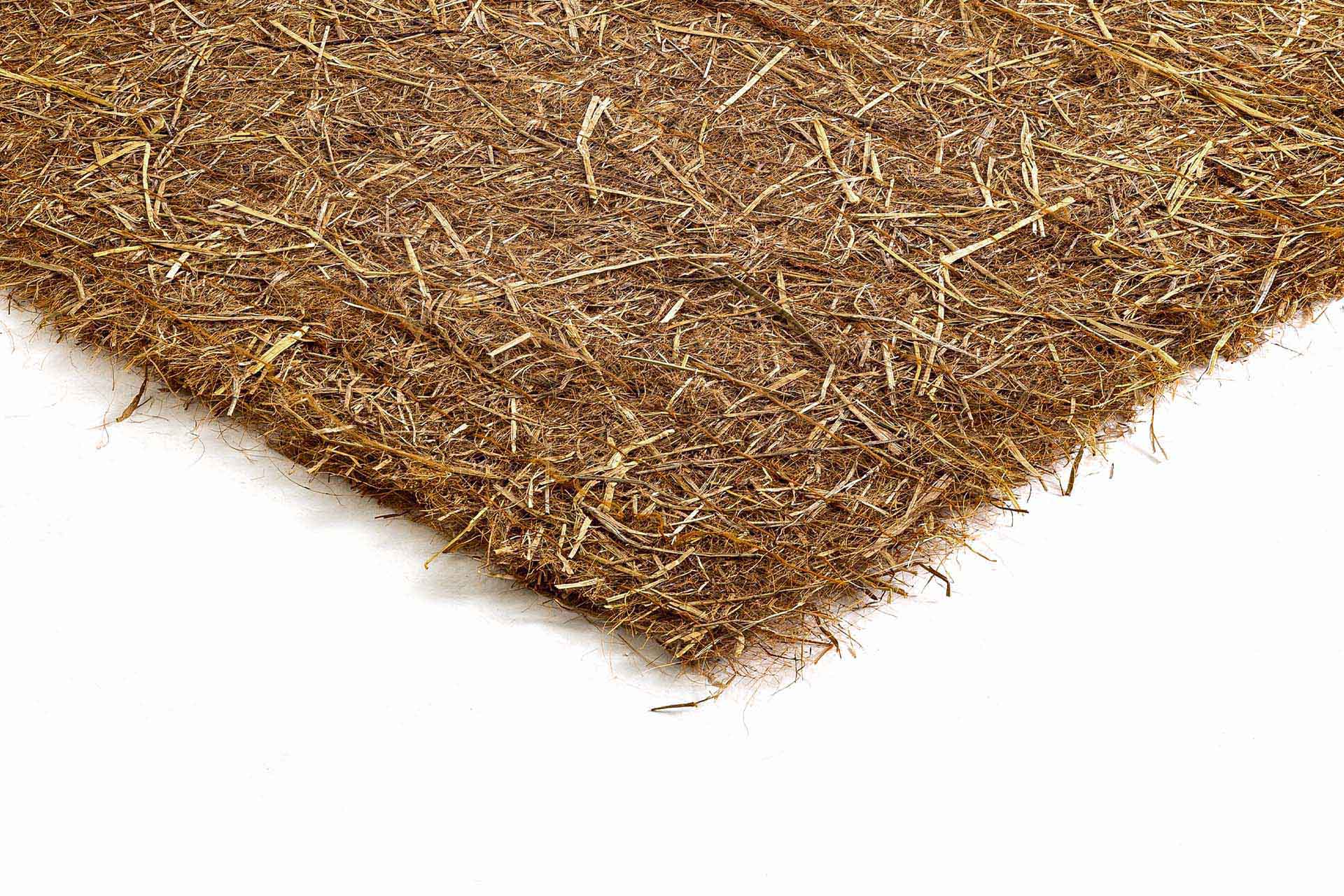
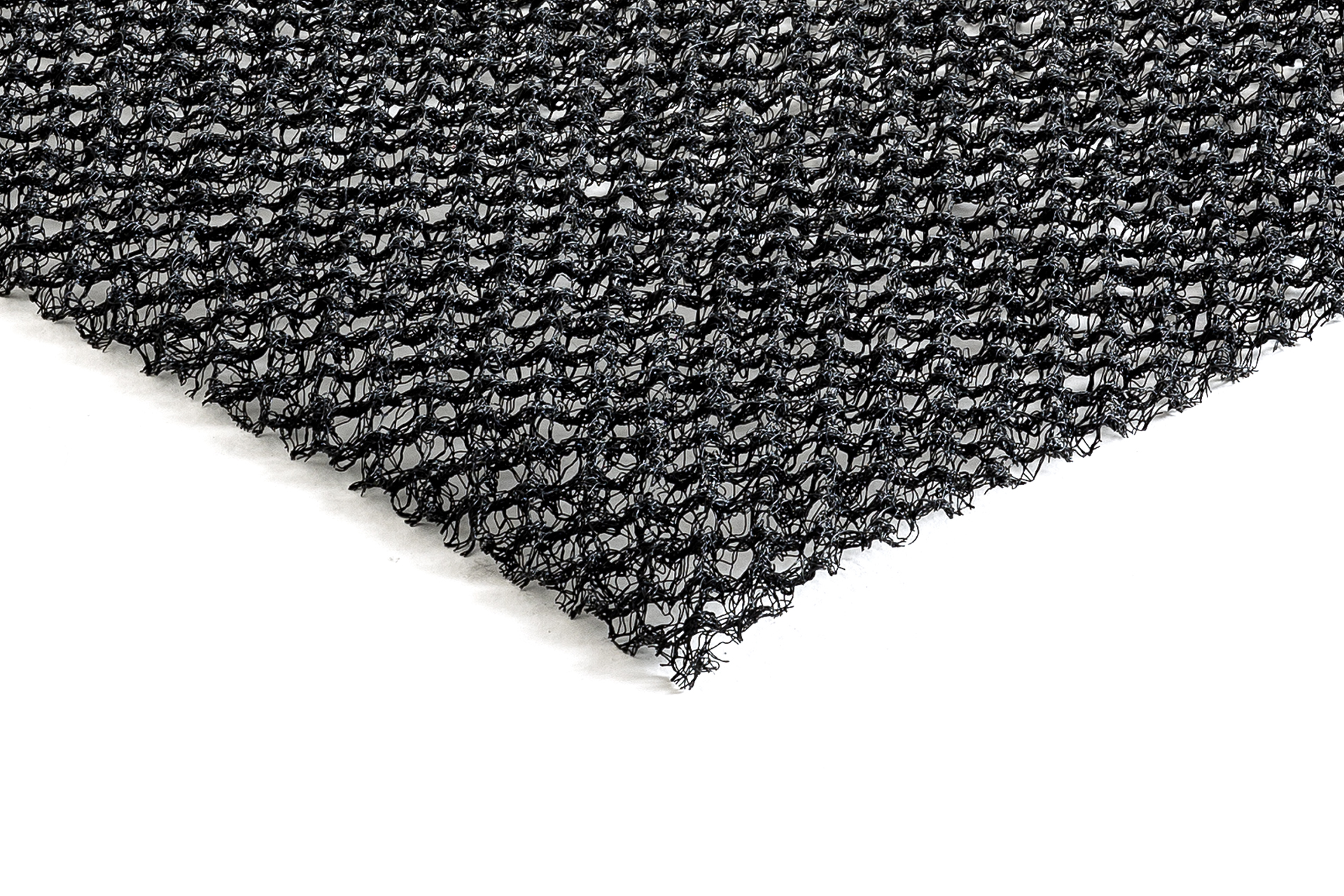
Vegetation naturally protects the ground from erosion by weather conditions such as wind and rain, which would cause subsidence. While waiting for grassing to protect the sides and surface of the landfill, anti-erosion geomats, in a biodegradable and synthetic version, can be chosen according to needs.
TeMa Geo Solutions offers a wide range to choose from, which can be browsed here.
Reinforcement
A landfill site is sometimes designed and built on more or less steep slopes. If a slope is steep and the ground is unable to support itself, retaining grids need to be installed in order to prevent slippage, which would expose and damage lower layers. View all our solutions.
Drainage
Specific products, drainage geocomposites, can be used for the drainage of rainwater and leachate, which inevitably builds up and must be kept away from the ground.
Barrier
Bentonite-based products, such as Barrier Bento, allow the area to be waterproofed, including walls with high slopes and the bottom.
Capping
Landfills also have a final cover that must meet precise criteria. These include isolating waste from the ground and surface erosion control. However, minimising water seepage and blending into the landscape are equally important.
- Published in GEO, Geogrids, Landfills, Landfills - Drainage, Landfills - Erosion control, Landfills - Reinforcement, Landfills - Waterproofing
New solutions in road construction and/or repairs
The safety of road infrastructures is the main goal, and maintenance work – whether preventive or supplementary – is systematic.
Road surfaces withstand heavy traffic loads and atmospheric changes with significant variations in temperature. Constant maintenance is therefore required in order to ensure even surfaces and the stability of structural elements.
Let’s look at the main factors involved in building new roads or maintaining roads.
Controlling surface erosion
Erosion is largely due to freeze/thaw cycles, which make asphalt less elastic and therefore more prone to internal voids. Such voids allow water to penetrate into underlying layers, gradually eroding the structure.
In addition, heavy traffic loads, especially heavy vehicles, cause deformation of the surface layers: this results in water penetration, which “softens” the structure and makes it less resistant.
Anti-capillary drainage
The water capillarity, i.e. the ability of liquids to move in micro-spaces even against the force of gravity, is a rather complex concept closely monitored in the construction industry. With the help of pressures exerted on lower layers, water rises upwards, dragging the finer components of materials with it and causing deformation.
It is therefore necessary to provide a drainage geocomposite, a three-dimensional membrane obtained by bonding two or more synthetic components in order to convey fluids to the exterior and prevent them from rising.
You can discover all our solutions here.
Reinforcement
It may sometimes be necessary to install reinforcement grids, especially if there is a more or less pronounced slope that would cause a road shoulder to slide downwards.
The choice of the most suitable type of reinforcement, and therefore also of the position of the geogrid in the layering, clearly depends on the problems to be faced i.e. reinforcing the surface area to limit the spread of cracks to underlying layers, improving the load-bearing capacity and reducing the stresses transmitted to lower layers, or providing a separation (and anti-contamination) function.
Discover all our solutions here.
Stabilisation
During intervention works, softer soils may be encountered, which may be subject to instability or even collapse in the early stages of intervention works. Even if this should not jeopardise the feasibility of the works, there is still the risk that the minimum legal safety requirements will be compromised.
Also in this case, geosynthetic products are the solution to the problem, as they absorb tensions at least until the intervention work achieves structural stability.
Discover the solutions in the X-Grid line here.
- Published in Drainage geocomposites and membranes, Erosion mats, GEO, Geogrids, Roads
Embankments in home gardens: small colourful islands
Made of masonry alone, embellished with different types and colours of plants and flowers, and of varying heights, embankments are often part of public buildings in parks and squares, but also a distinctive feature of private gardens. In the urban construction context, embankments can be borders for roadside verges, steps and flowerbeds, reaching a relatively low height, almost always less than 1 metre.
The provide a very attractive and organised visual effect and can be customised with the colours and types of plants you prefer. However, in order to achieve adequate stability for such intervention work, regulations require certain specifications to bear in mind for their construction.
A short and simple recap: let’s start by understanding what they are and how they are built.
What are embankments?
Embankments are accumulations of earth that form more or less evident differences in the level of the ground and can be natural or artificial. Natural embankments are caused and possibly accentuated by landslides, whereas artificial ones are man-made and consist of an earth fill supported by a wall, often in order to highlight the difference in level.
The risk of landslides
As mounds of earth, especially if they are of a certain height, embankments can be severely tested by atmospheric events, resulting in erosion and runoff due to rainwater.
Various characteristic elements can therefore be recognised:
- drainage and runoff systems in the underlying area where all rainwater accumulates;
- support and reinforcement of slopes, the part most susceptible to erosion;
- substrates and erosion control systems to allow plants to grow in the best conditions by sheltering the topsoil from the effects of the wind, sun and rain until the plants have become strong and well-rooted.
Block retaining walls and reinforcement grids
In order to prevent soil erosion or irrigation, embankments are reinforced with retaining walls in a combination of concrete blocks and geogrids, which meet geotechnical, building and architectural requirements.
TeMa Geo Solutions has the right products to create this type of construction.
For soil reinforcement we suggest X-Grid, reinforcement geogrids, which are knitted uniaxial geogrids made of high tenacity polyester yarns covered with a protective PVC layer.
For retaining walls, the range includes T-Block, a single concrete block for building reinforced walls.
The special feature of this product is the male/female joint, shaped directly on the block. This ensures maximum connection between the blocks, thus avoiding the use of mechanical fasteners, glue or mortar and making the wall stronger and more resistant to damage.
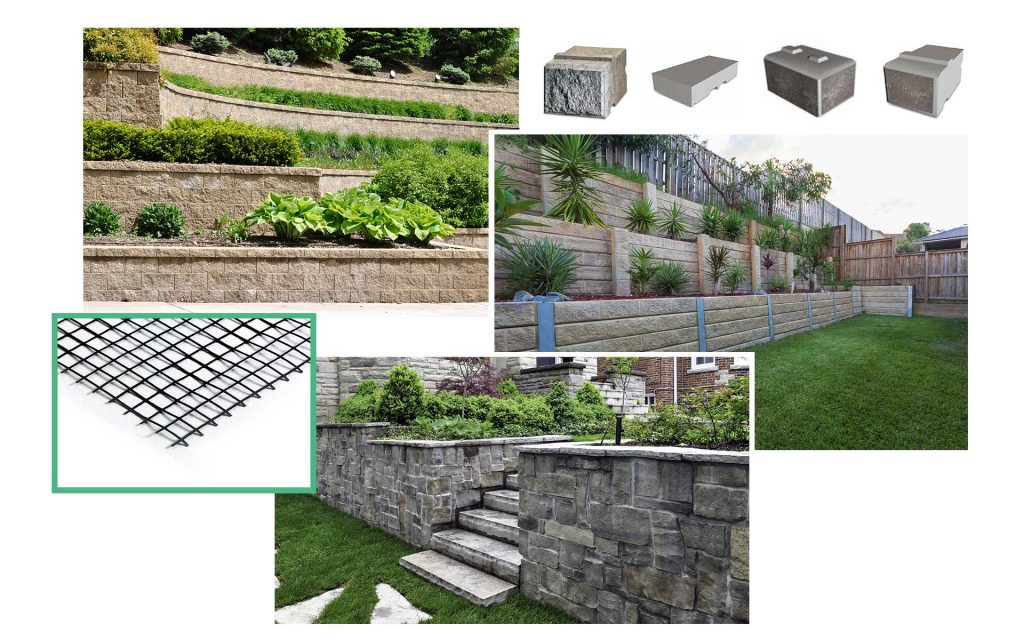

Find here all the specifications of the products mentioned.
Protecting the vineyard landscape: tried-and-tested technologies… sitting lightly in the field.
The photo conjures up a lofty tale: “Autumn arrives and with it, the first rains, days draw in, the temperature starts to drop and, above all… it’s harvest time!”
We’re in the eastern corner of the Veneto region, the Prosecco hills have outdone themselves once again this year and a steady stream of grape-laden trailers continue to roll past on their way to the wineries. But this year’s harvest has had to contend with rather uncertain weather patterns: frosts in late spring, persistent rain interspersed with dry spells, with violent storms and hail over summer.
These conditions certainly don’t help the soil, putting it at risk of slips, subsidence and erosion. But if we apply TeMa Geo Solutions’ modern technologies and materials designed for this very purpose, we can protect the land from damage and, what’s more, do it in a sustainable way.
Not far from here, just a few kilometres from our headquarters, the Prosecco hills fall largely within the UNESCO World Heritage Site, meaning any measures must be strictly reconstructive, designed to protect the status quo and absolutely non-invasive: “gentle” on the environment.
TeMa Geo Solutions has come up with high-performance solutions to control the natural erosion of the soil, reinforce slopes, and drain water with:
- biodegradable fibre matting made from 100% natural jute such as Ecovernet® J500 XL and Ecovermat P Grass, which provide protection to stop soil being blown or washed away by the elements, and encourage vegetation;
- the K-Mat F erosion control synthetic geomat;
- reinforcement geogrids such as X-Grid PET PVC, which can withstand considerable stress levels;
- the Speedrain drainage geocomposite, which drains away water from the surrounding soil, stabilizing any surface slips.
Products
If you wish to receive more information, CONTACT US or take a look and download our “Vineyards” catalogue.
Geosynthetics: Advantages and Applications
Our passion for work does not stop, it simply continues at our company, in a little more limited way. You certainly cannot see us running up and down building sites or going in and out of our research labs, but we can assure you that we are still working on our production of geosynthetic products with the same commitment and perseverance in order to formulate new projects and develop ideas that we will see materialised soon, once everything has ended.
TeMa and Geosynthetic Products
TeMa Geo is the TeMa division created almost thirty years ago with the aim of exploring and expanding the world of geosynthetics, which it still does today. By “geosynthetic products” we generally mean all categories of synthetic coverings that are not only used in contact with earth or other building materials but are also appreciated for their use in various building fields. In the building industry, their main advantage is that they are user-friendly in technical terms, which is why engineers and planners prefer them to other technical solutions.
The Advantages of Geosynthetics
The advantages of geosynthetic options not only lies in the fact that they are easy to use but also in their cost-effectiveness: certainly less expensive, they provide excellent performance that remains unchanged over time. Furthermore, their versatile use makes them the ideal solution to various on-site problems.
Geosynthetic Products “In the Field”: the Serravalle Project
In more practical terms, today we want to tell you about the intervention works we carried out in the Piedmont region in 2016. It involved extension works for Serravalle Retail Park. In preparation for the works, we had to make the slope in front of the new complex safe. In order to proceed, we had to prepare several reinforced soil structures, separating them into banks, and solve the problems of surface drainage for the management of water, whose catchment area was located above the area.
For works of such magnitude, we used geogrids from the XGrid PET-PVC range as a structural element. In addition, to avoid any seepage in the future, drainage elements were installed close to the reinforced structures of the horizontal sections of each berm. This is just one of our products and one of the many fields of application explored by TeMa.
To discover all our membranes, visit our section dedicated to products.
- Published in GEO, Geogrids, Reinforced earth structures, Reinforced earth structures - Drainage
Cycle/pedestrian paths: when we get back onto our saddle, we’ll know more about them…
We know that our bike has become a mirage. But we can promise ourselves to use it more when this period of seclusion is over. Meanwhile, why don’t we take advantage of the time available to discover interesting things all around us? For example, cycle paths. Let’s start at the beginning.
What is the correct definition of a cycle/pedestrian path?
It’s where you can ride your bike, of course. But, can pedestrians walk on it too? What is the direction of movement? Then there are increasingly more complex questions, such as: has it been built as a separate cycle path or as a reserved lane? Is it a cycle/pedestrian path or a vehicular/cycle path? In short, there are many features that a cycle/pedestrian path must have in order to be defined as such. Let’s take a look at them together.
The cycle/pedestrian path was invented to allow pedestrians and bikes to get about. Such paths require cyclists to respect pedestrians and get off their bike whenever necessary to avoid getting in the way. Consequently, they are not paths for the exclusive use of cyclists.
Creating these kinds of paths encourages people to get about without using a car, thanks to these dedicated spaces, where they can feel safe from urban traffic.
How do you build a cycle/pedestrian path?
In 2018 TeMa Geo Solutions built a cycle/pedestrian path in Cozzuolo di Vittorio Veneto (TV). One of the main aims of the project was to improve road safety in an area that is a gateway to the city and where a city park is situated, used by families and children.
First of all, we enlarged the road and the nearby roundabout in order to create the necessary space for inserting the path. The enlargement was facilitated by the construction of a reinforced earth escarpment, for which reinforced geogrids were used. Installed in the ground, they create friction and enable the system to withstand significant levels of stress. The intervention work, designed on the basis of a single berm positioned at about 2 metres above ground level, allowed pedestrian and cycle traffic in an area that had been dangerous from the outset.
Looking on the bright side, when you get back onto your saddle, you’ll be more aware of what’s under your wheels. Enter the TeMa world, visit our website.
Multiple interventions… Mainly in the private sector
In 2018, we were called to a private house in Pordenone. As a result of sudden and severe meteorological events, the escarpment behind a reinforced concrete retaining wall collapsed. We were quick to intervene to avoid any kind of damage, since the house was under construction and the environmental impact had to be almost minimal.
SOLUTION ADOPETD
We therefore decided to use our PET-PVC 55 XGrid, the uniaxial woven PET geogrid that provides new stability for soil. It is a reinforcement geogrid made of polyester synthetic yarns, obtained by weaving, which is highly resistant and coated with a protective layer (PVC). Uniaxial PET-PVC XGrids are used to implement soil reinforcement support works, whereas biaxial XGrids are used for soil reinforcement and stabilisation.

Uniaxial PET-PVC XGrid
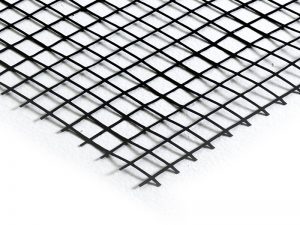
Biaxial PET-PVC XGrid
TeMa GEOSYNTHETICS
TeMa Geo Solution has the mission of intervening on the environment using geosynthetic products and the lowest possible impact. This goal is pursued by researching and inventing new products for environmental engineering, actively involving planners and companies while assisting customers in the pre-sale phase and during and after installation.
Thanks to a modern integrated production system with branches in Italy, Spain, Turkey, Russia, Romania and the USA and a widespread sales network in more than 60 countries, TeMa offers tailor-made solutions for all projects involving structural, protection, maintenance and safety elements in the residential and civil building sectors and in the field of major environmental works. Furthermore, TeMa is not only involved in the industrial building field but also in the private building one.
This is just one of many stories we could tell you about our company, which focuses on technological innovation, ongoing research and territorial responsibility.
- 1
- 2