Damp, rising damp and efflorescence in basements.
Damp, mould, stains and flaky plaster in basements are a homeowner’s worst nightmare. We’ve mentioned numerous times that weather events and groundwater, where not controlled properly, are the main cause of damp. Of course, it doesn’t just affect the walls, but the whole structure, including flooring, on the basement level or even on the ground floor.
The phenomenon that’s so often underestimated is so-called “rising damp”, which occurs when water under the ground enters walls as a result of direct contact and is pushed upwards by capillary action, allowing the moisture to rise around ten centimetres or more. The moisture can even climb metres up the wall by “latching on” to molecules of a different kind, in this case those of the actual walls. The damage caused by the abnormal increase in moisture inside walls is immediately visible on the walls of ground-floor rooms or basements.
What effects the water’s capillary action has
The effect of capillary absorption manifests in the form of:
- static damage to the building, which is weakened and becomes less safe
- worsening occupant comfort as a result of unhealthy, smelly rooms
- cosmetic damage, with the appearance of stains and peeling plaster
- higher heating costs due to the lower surface temperatures of internal walls
- efflorescence
- a capillary action that causes water to rise through walls, bringing with it salts from the ground that, once they crystallize as a result of the evaporation process, swell and cause paint and plaster to peel: white stains forming around cracks are known as salt efflorescence.
The effects are less visible when the surface affected is flooring, with symptoms like swelling, salt efflorescence, mould or changes in the colour of grout often only appearing later on.
All these issues derive from the misguided choice of materials, or poorly designed and executed work, often compounded by the fact that the foundations’ waterproofing is damaged or even non-existent. This is not an issue linked to weather events, rather it stems from the presence of groundwater.
How TeMa Building Solutions can help
Both rising damp and efflorescence issues can be prevented with the use of suitable materials. TeMa Building Solutions offers an extensive range of studded membranes and drainage geocomposites to remove water before it comes into contact with the structure and to provide waterproofing with reliable, lasting protection.
Our engineers are here to help you choose the right specific product for your next project.
Contact us!
- Published in BUILDING, Drainage geocomposites, Foundation and underground structures, Foundation and underground structures - Damp proofing systems, Foundation and underground structures - Drainage systems, Foundation and underground structures - Systems for mechanical protection, Foundation and underground structures - Systems for Waterproofing
Solutions for protecting foundations and below-grade walls
The health of walls in contact with the soil — like foundations and below-grade walls — is the primary concern of the home’s occupants, especially where underground garages or basements are involved: any sign of damp or mould is evidence of damage that can have serious financial consequences in these areas of the building. And restoring the interior to good health is not always feasible.
The risks lie both in the foundations — namely in the horizontal structures that receive and absorb the loads of the whole building — and in the below-grade walls, namely the vertical structures that have to withstand considerable loads. If we take the worsening weather patterns of recent years and add in pesky capillary rising damp, and groundwater pressure, there’s clearly a need to ensure the products used provide improved performance.
How do we best protect foundations and below-grade walls?
The way to keep underground rooms healthy is to use specific, tried-and-tested products, applied correctly as per the technical literature. TeMa Building Solutions has various solutions on offer.
Bentonite geocomposites
Bentonite geocomposites can be used to ensure the concrete is properly waterproofed. Comprising natural sodium bentonite, they self-bond to concrete (if used as waterproofing prior to insitu casting) and are suitable for both vertical applications (below-grade walls) and horizontal applications (slab foundations).
Studded membranes
Studded membranes are one of the most widely used products given their dual function:
- they mechanically protect waterproofing: they prevent damage to the waterproofing layer during the backfilling and compaction process at the construction phase, and protect from the subsequent micro-movements as the soil settles, and the considerable loads that the walls have to withstand
- they serve as damp-proofing: they stop moisture, which — even in the absence of hydrostatic pressure — can undermine the structure and cause patches of mould to appear on internal walls.
Drainage geocomposites
They reduce hydrostatic pressure exerted on vertical walls, conveying water away from the walls to the outer perimeter. They are laminated with one or two nonwovens serving as a filter layer, stopping the system becoming clogged. The TeMa Building Solutions range includes geonets, studded membranes and monofilament structure.
Need help choosing the right product? Contact us! Our experts are here to help you any way they can.
Use of drainage geocomposites in building
Serving multiple functions, drainage geocomposites are a perfect match for geotechnical applications, while they have a number of distinctive properties making them a popular choice in the building industry, too. TeMa drainage geocomposites are light, easy to handle both by carriers and on site, quick to apply… But let’s take a look at the full picture in detail.
What are drainage geocomposites and what different types are there?
Drainage geocomposites are, by definition, permeable geosynthetics comprising at least two elements (one synthetic element and one or more nonwovens).
TeMa offers three main types of drainage products, which all come with the benefit of its considerable experience:
- Geonets, made up of a synthetic HDPE mesh comprising two criss-crossed strands sandwiched between two PP nonwovens to which the mesh is thermally bonded, like T-Drain.
- Geomembranes like T-Kone and TMD, HDPE studded membranes with different stud heights (8, 10, 20 mm) laminated with a nonwoven.
- Monofilaments, made up of an extruded synthetic monofilament core sandwiched between two nonwovens to which the core is thermally bonded, such as T-Mix Drain.
What are their possible applications?
The drainage geocomposites from TeMa Building Solutions cover numerous applications: pitched roofs and ballasted flat roofs, flat green roofs and trafficable flat roofs, standing seam metal roofs and walls, foundations and underground structures, and damp-prone internal walls.
These are all applications that require special attention to drainage as they are exposed to different weather conditions and, in some cases, to groundwater as well: the risk of ponding increases, encouraging damp and, if the waterproofing layer becomes damaged or has too much pressure on it, water seepage and leaking can become an issue.
What purposes do drainage geocomposites serve?
Their main purpose is draining rainwater and groundwater. This is achieved by the action of separation, made possible by the nonwoven, which acts as a filter: the particles that manage to get through it are so extremely small as to have no effect on the proper functioning of the drainage system.
The studded membrane geocomposites also serve the important purpose of providing mechanical protection for waterproofing, which is valuable in roofs and simply essential in underground structures if they are to cope with backfilling and settling of the backfill without being damaged.
Which drainage geocomposite should you choose?
To choose the right product, you need to look at what performance is required. Designers know this well: it depends on the amount and “quality” of water to be drained, and hence on the morphology of the site, whether there are active aquifers, and so on. Loading is another factor to be taken into consideration, in such applications as green roofs, as well as for trafficable roofs and walkable surfaces.
- Published in BUILDING, Drainage geocomposites
Reinforced earth retaining walls: specific products for each function
The function of retaining wall structures is to retain and reinforce soil faces. They can be built in a multitude of areas, including private ones such as gardens and vineyards, as well as public areas such as roads, railways and embankments.
They meet the need to recover usable spaces as they can also be built with a steeply sloping face.
The authentic green appearance
Nowadays, the modern building industry is highly aware of sustainability and territorial integration. Under certain conditions, reinforced earth retaining walls can replace conventional concrete walls, without underestimating the aesthetic appearance of the landscape. This is even more important in areas subject to landscape restrictions that require the preservation of natural aspects using specific materials and construction techniques.
TeMa Building solutions integrate these trends by catering to various problems concerning land conformation and hydrogeological protection.
The functions of reinforced earth retaining walls and the products required to achieve them
Slope gradient, exposure to weather conditions (including severe ones) and the mechanical properties of the terrain often require technical solutions that stabilise a slope. Synthetic products can be used, each one performing a specific function.
Reinforcement with geogrids
The compressive strength of the soil is combined with the tensile strength of the geosynthetic product (such as T-Grid). The friction involved develops a tensional state that stabilises the structure.
Profiling with formwork units
Electro-welded metal structures such as formwork units provide a shaping of the soil face up to a 65° slope.
Controlling surface erosion with erosion control mats
Severe or prolonged weather conditions, such as strong winds and sudden downpours – and the resulting surface run-off of water – could lead to erosion and depletion at the face of reinforced earth layers, particularly if they are fully greened. The solution to this problem is to use, on the face of each layer, three-dimensional synthetic mats such as T-Mat made of polypropylene or K-Mat FG Green made of fibreglass. Alternatively, natural, biodegradable mats made of jute fibre such as T-Juta 500 can be used (also available in an XLversion).
Soil containment using gabions
An alternative solution to reinforced earth walls can be found in walls built using double-twisted wire mesh gabions, such as T-Gabion, filled with pebbles. Gabions are also an interesting solution for smaller residential projects: they provide containment while offering a different and innovative aesthetic appearance.
- Published in BUILDING, Retaining walls, Retaining walls elements
Ballasted roofs: why gravel, and how to protect their waterproofing
Something of an innovation in the Italian building scene, while also being a useful device for protecting the roof, the ballasted flat roof is a solution that can become a distinctive feature of either a residential or commercial building.
Unlike the traditional system involving the use of concrete, using gravel is an option that brings a number of attractive advantages:
- it protects the roof against wind and UV rays
- it protects the roof against mechanical damage
- it is low maintenance
- it provides thermal comfort in summer as it shades the roof
- it makes the whole roof system practically fireproof
- it is long lasting.
In building, the choice of a ballasted roof is often prompted by aesthetic reasons for a holiday home or a hotel by the sea, or in an area with high sunshine hours… while it also caters to the need for optimal insulation and low maintenance.
The TeMa Building Solutions answer for protecting ballasted roofs
When gravel is laid, the load can tear the waterproofing layer on the roof underneath, and this comes with the risk of leaks, with all the ensuing stain, mould and structural damage issues.
So it is important to address the need for rainwater drainage and mechanical protection of the waterproofing.
TeMa Building Solutions has come up with a product that serves multiple functions: the product in question is T-Kone G Drain, the studded membrane (which serves to protect the waterproofing) featuring a geotextile (addressing the need for filtration and separation).
Placed between the gravel layer and waterproofing, T-Kone G-Drain is thin, strong and ideal for an effective build-up without the bulk.
- Published in Ballasted roofs, BUILDING, Studded membranes and accessories
Green surfaces and green roofs: benefits and technical ins and outs
In recent years, “green” has become more and more of a buzzword, encompassing simple and cost-effective solutions that can be adopted by anyone with a roof. We’re talking green roofs, which, in addition to bringing undeniable environmental benefits, are the perfect place for relaxing with the family or enjoying summer drinks with friends. The origins of roof gardens date back to ancient times — think Hanging Gardens of Babylon — and, today, are built for extreme reliability, including long service life, with excellent products producing even more advantages.
Let’s take a look at the full picture in detail.
The advantages of green areas
For the environment
Plants and grass are natural carbon sinks, absorbing CO2 and releasing oxygen, in addition to filtering particulate matter. In addition, they lessen the urban microclimate effect by lowering temperatures by several degrees centigrade, and reduce electrosmog caused by any electronic device.
They muffle noise and, if designed well, absorb and retain the early sudden downpours associated with significant rain events.
A series of sustainable improvements for urban wellbeing, improving air quality with less smog and particulate matter.
For occupant comfort
Vegetation also acts as natural thermal insulation — which is no small advantage given the energy crises of recent months — and soundproofing in loft bedrooms. Furthermore, it provides the roof with effective protection against UV rays, mechanical stress and daily variations in temperature, thus increasing the average service life of waterproofing.
Lastly, creating a garden on a roof increases the value of the property.
From a technical point of view
A green roof build-up comprises a number of layers, including geosynthetics offering better performance than traditional systems in terms of drainage, mechanical protection of waterproofing, and filtration. The products used are lighter and non-bulky, easy to transport and quick to install.
Functions required of the roof
There are 4 main functions involved:
- Reservoir (to hold rainwater for irrigation purposes until it is needed) and drainage (to remove excess water). This combined function is addressed with 20mm HDPE studded membranes T-Kone H XL and T-Kone H XL S.
- Control of surface erosion caused by atmospheric agents. This function is addressed with natural fibre matting T-Juta 500 and the synthetic geomat T-Mat.
- Drainage. This is where T-Mix Drain 20 SS comes in, the cuspated-fibre geomat sandwiched between 2 geotextiles.
- Mechanical protection of waterproofing. The geotextiles from the Tematex NW PET range, in white and black, fit the bill.
- Published in BUILDING, Flat green roofs
Tips for the correct laying of TMD 1011
For vertical applications, such as foundation walls, and for horizontal applications, such as flat roofs, mechanical protection of waterproofing is required and, often, also drainage: TMD 1011 is a studded membrane, produced by TeMa Building Solutions, that performs both functions: drainage for vertical applications and waterproofing protection for horizontal applications.
A few tips for laying TMD 1011 on horizontal surfaces
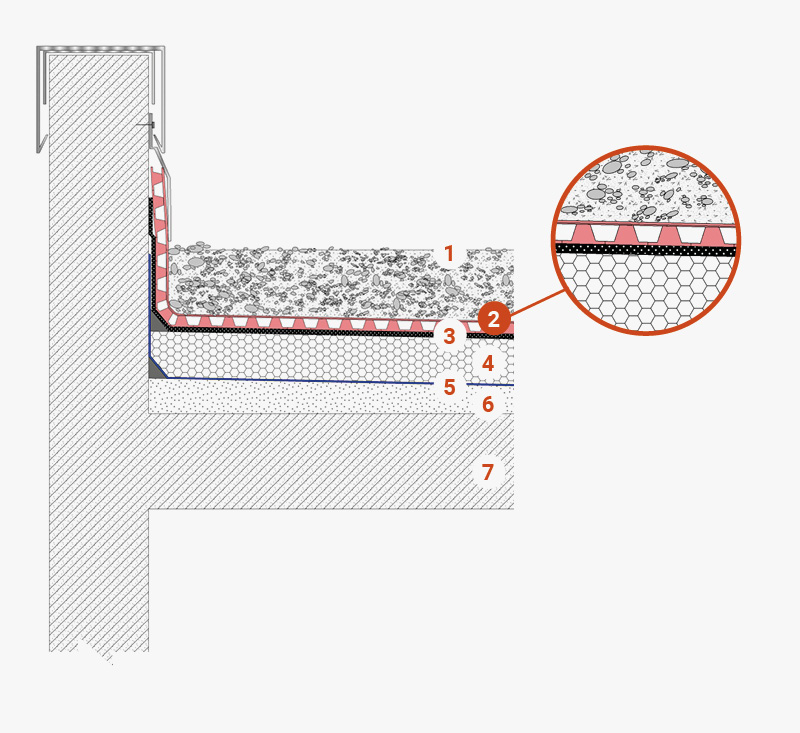
Flat roof with gravel finish (weighted)
1 Gravel finish
2 TMD 1011 membrane serving as a drainage layer and for waterproofing protection
3 Waterproofing membrane
4 Thermal and acoustic insulation
5 Vapour barrier
6 Sloping underlayment
7 Load-bearing structure
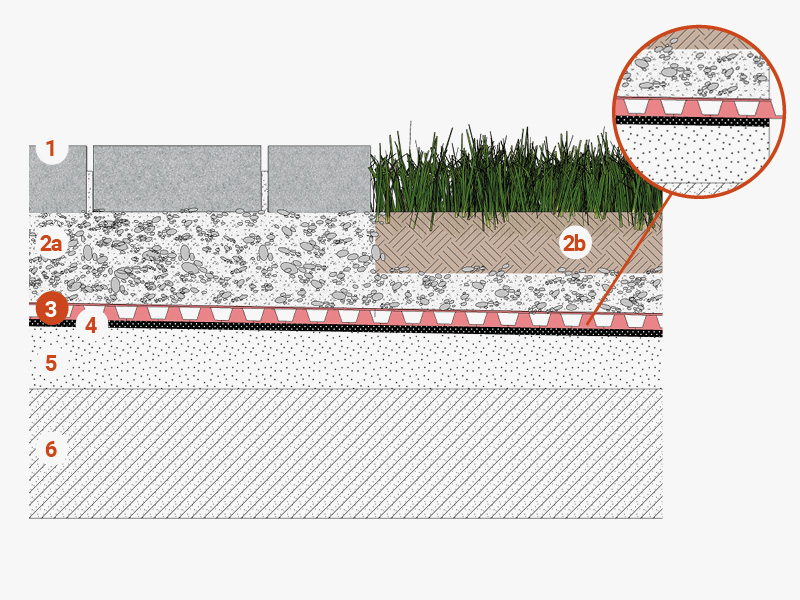 Walkways and green areas
Walkways and green areas
1 Interlocking block paving
2a Crushed stone bedding course
2b Growing medium
3 TMD 1011 membrane serving as a drainage layer and for waterproofing protection
4 Waterproofing membrane
5 Vapour barrier
6 Sloping underlayment
7 Load-bearing structure
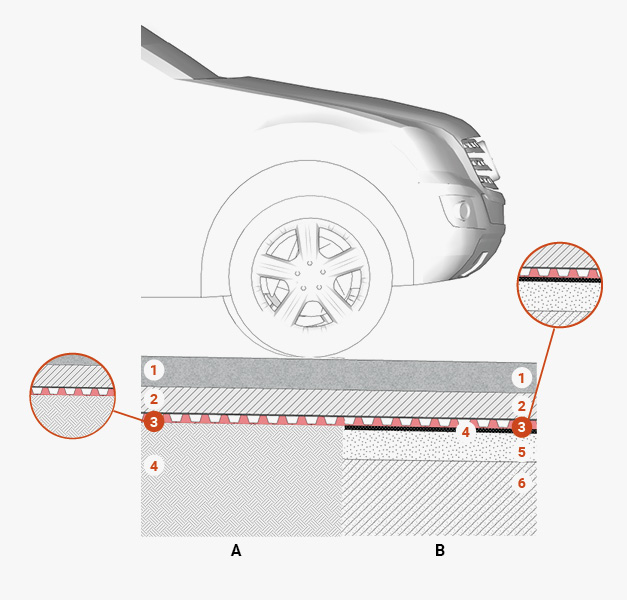
Surfaces suitable for vehicle traffic A
1 Paving designed to take vehicle loads
2 Sand bedding layer
3 TMD 1011 membrane serving as a:
– drainage layer
– substrate in place of traditional concrete levelling compounds
– separating and leachate containment layer (oils or hydrocarbons)
4 Substructure / ground
Surfaces suitable for vehicle traffic B
1 Paving designed to take vehicle loads
2 Sand bedding layer
3 TMD 1011 membrane serving as a drainage layer and for waterproofing protection
4 Waterproofing membrane
5 Sloping underlayment
6 Load-bearing structure
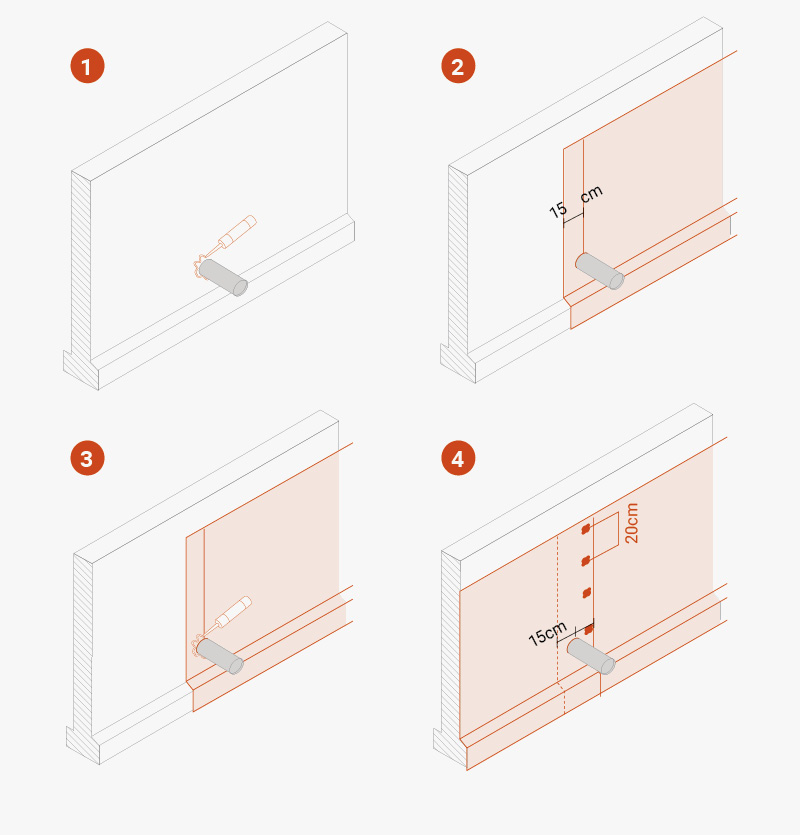
A few tips for laying TMD 1011 on vertical surfaces
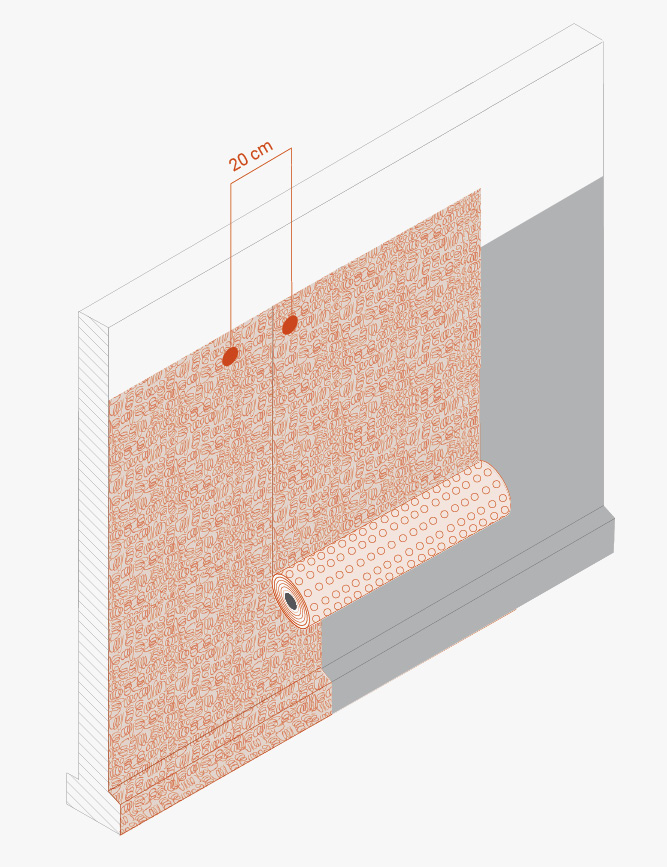
Unroll the membrane and install it vertically or horizontally: in the latter case, the width of the roll corresponds to the height of the wall to be protected. Two consecutive membranes should overlap by about 20 cm, and the studs should interlock.
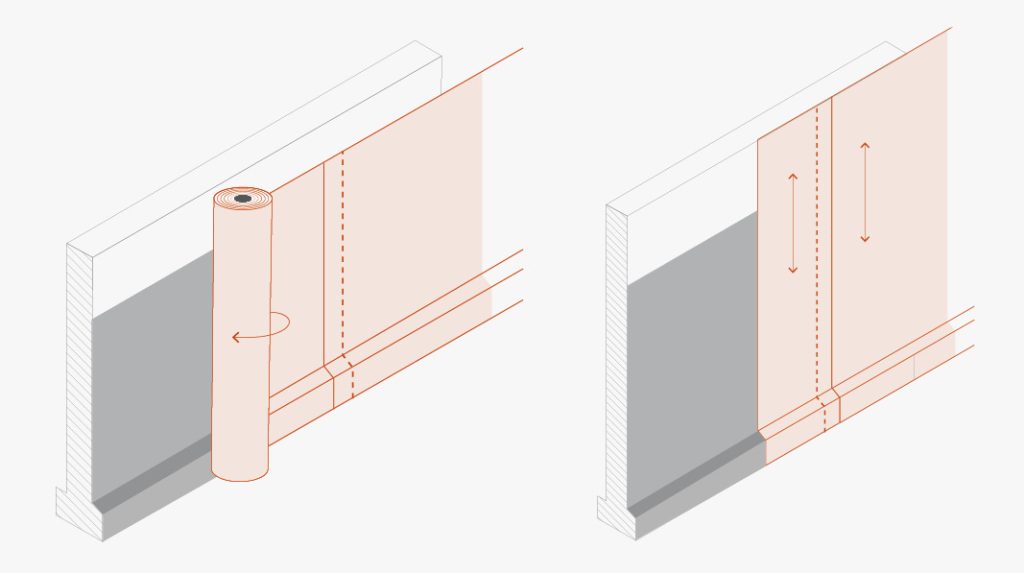

For horizontal joints, if the TMD 1011 membrane is not wide enough to completely cover the height of the installation, the first layer should be installed from the base upwards and then, keeping an overlap of at least 15 cm, the second layer should be installed by overlapping the first layer outwards (i.e. towards the side away from the wall). Install washers every 20 cm in the overlapping area.
Inlets for utility connections, such as water, gas, sewers or similar pipelines
- Place mastic sealant around the pipeline or inlet.
- Cut the TMD 1011 membrane vertically so that it extends 15 cm beyond the pipeline or inlet, trimming the membrane so that it adheres as tightly as possible.
- Put mastic sealant on the membrane so that there is a layer of mastic both above and below the membrane around the pipeline or inlet.
- Start the next installation of the membrane 15 cm before the pipeline or inlet so that the overlap around the pipeline or inlet is 30 cm. Trim again around the pipeline or inlet for watertightness.
- Install fasteners every 20 cm along the edge of the overlapping membrane.
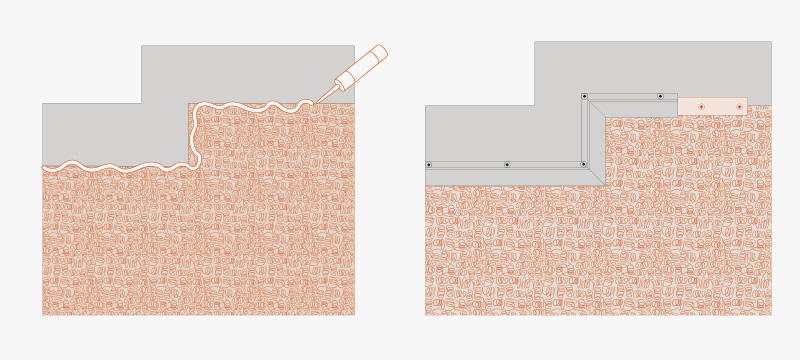
Change of level or areas where the smooth part has been trimmed
Use T-Profile + T-Nails to seal the edge, using a sealant for the area to ensure that the edge is properly sealed.
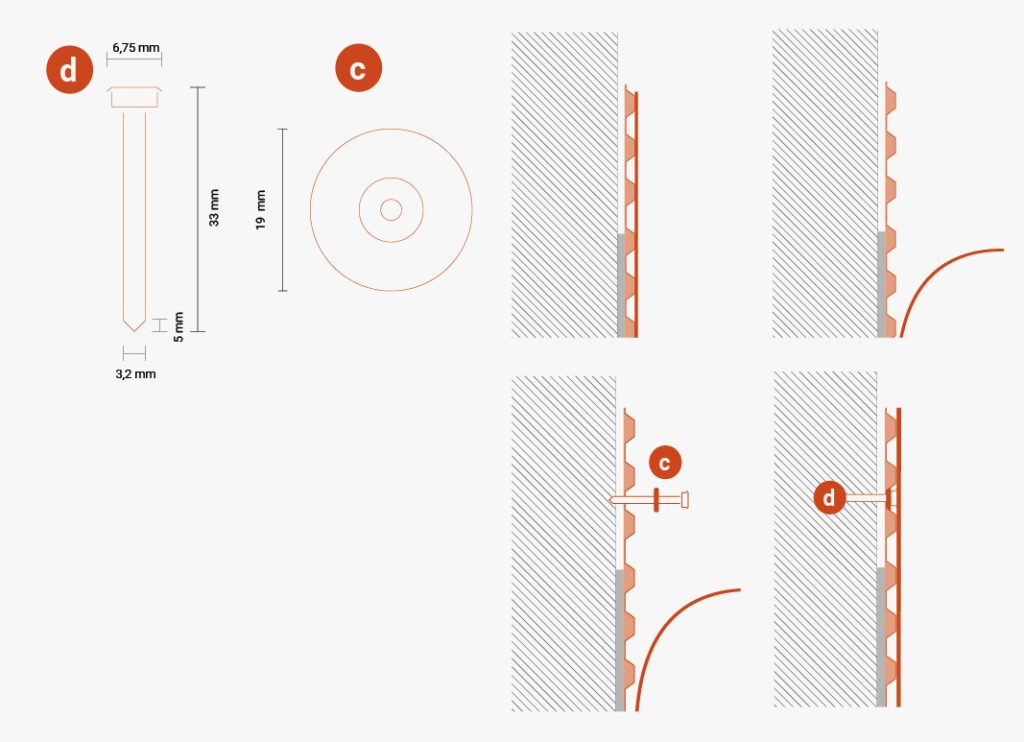
TMD 1011 should also be protected with T-Profile to prevent soil from penetrating into the gap between the wall and membrane. Then, fasten it using washers and nails with T-Nails spaced at intervals of 20-30 cm, either along the upper edge of the studded membrane or along the profile.
Drainage for diaphragms and berlin walls: a practical and safe solution
Some of the most widely used works in the civil engineering field are diaphragms and berlin walls, which counteract strong thrusts of the soil and prevent landslides and structural subsidence.
Diaphragms are supporting walls consisting of pointed vertical elements (piles) or continuous elements (walls) made of steel or reinforced concrete. They are driven into the ground to a considerable depth, whereas Berlin walls are flexible retaining structures constructed with vertical micro-piles.
Both solutions are used where it’s impossible to construct excavation walls of an adequate gradient due to the presence of other nearby structures and to the morphology of the area , which imposes limited work spaces (that would make manoeuvring large machinery impossible).
Berlin walls made of micro-piles are one of the most popular applications on construction sites for implementing waterproof retaining works. The technique allows work to be carried out on almost all types of terrain, especially when it’s necessary to use on-site systems that are smaller than in the past.
Since works are in contact with the ground, the drainage aspect should not be underestimated. If rainwater and groundwater exert pressure on the vertical wall, they may damage the waterproofing. TeMa Building Solutions therefore has the right product for this application: T-Mix Drain WP, the geocomposite that not only drains but also provides the functions of filtration, separation and stay-in-place formwork.
TeMa has acquired considerable experience with geocomposites. For many years, the company has been providing this system to replace the conventional gravel drainage system. The results are long-lasting and it’s the ideal solution: compared to conventional gravel, it’s less bulky, easily transported and quick to install. This reduces the costs of transport and implementation and on-site construction time while, last but not least, resulting in considerable savings in terms of CO2.
Fields of application
As mentioned above, diaphragms and berlin walls are widely used where space is limited. More specifically, they can be used in the construction industry, for example for underground garages in homes or commercial premises, for basements. They can also be used in river works, such as quays and piers for boats, or in earth dams and wells.
Having the experience of TeMa technicians and tested effective products such as T-Mix Drain WP at your disposal is therefore a guarantee for your construction site.
Waterproofing when concrete casting
Concrete casting involves creating a new concrete element as a continuation of an already existing one. Most often it’s impossible to create a monolithic block with a single casting: consider, for example, very large structures or the connection between vertical and horizontal walls. With concrete casting you can obtain monolithic structures with their own characteristics, built in stages at subsequent times. So, you proceed with small blocks and join each casting to the previous one, creating a monolith piece by piece.
Structural connection is achieved by using reinforcing irons, taking special care with drilling the existing block and the length of anchorage. While ensuring attachment to the sequence of blocks, reinforcing irons are potential lines for water seepage. We well know that accumulation of moisture in walls may have very severe consequences: structural fragility and very unhealthy stains and moulds.
An effective solution is to insert bentonite kerbs which waterproof any voids that may have formed at the base of walls or in contact with reinforcing irons. The intrinsic property of sodium bentonite is exploited, which is the ability to swell on contact with water, filling the available space and forming an impermeable compound.
Furthermore, this material provides high resistance to hydraulic load, is easily applied and adheres perfectly to the support.
The range of building products from TeMa Building Solutions also includes T-Bentostop, the waterstop made of hydro-expanding bentonite for waterproofing and sealing concrete casting.
Concrete industrial paving: How to ensure versatility and durability
A factory layout determines the physical positioning of machines, workstations that develop individual processes and service departments in order to make the work of people, machines and materials more efficient.
Paving is subjected to continuous stress and have to withstand considerable loads. Concrete has its own characteristics to meet these needs and is also very aesthetically versatile, which means that it’s often used by designers in domestic and commercial contexts, both indoors and outdoors. Moreover, it can be quickly customised with textures or other types of printing.
What functions are important in industrial contexts?
Industrial paving inevitably suffers wear and tear from prolonged and intensive use.
It is therefore necessary to guarantee high compressive strength. This is because the surfaces of environments such as warehouses and industrial facilities are constantly subject to heavy loads: storage shelving systems, machinery and moving vehicles such as pallet stackers and forklift trucks. In many cases, weights are concentrated more in some places than in others (e.g. the areas where pallet stackers move or the quintals of goods in the warehouse that weigh down on the same spot for a long time).
This can also cause fissures and cracks on the surface that would hinder access and make it difficult to carry out normal work activities.
Lastly, as already mentioned, concrete is a very versatile material that can be laid over other types of substrate and also customised as required.
How to achieve an optimum and long-lasting result?
Thorough planning from the outset and the choice of suitable materials is the first step to a successful result, but painstaking attention during laying is also important.
The product range from TeMa Building Solutions includes specific products for the reinforcement of this type of paving. T-Fiberglas CLS mesh, made of fiberglass and coated with a special alkaline dressing, is designed to reinforce horizontal concrete applications, whereas T-Zink Net is the anti-cracking mesh made of galvanised steel.
- Published in BUILDING, Concrete paving











